What is the Net Investment Income Tax? Definition, Purpose, and Scope: Ever heard of the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT)? It’s a tax that applies to high-income individuals who have investment income exceeding certain thresholds. Imagine you’re rolling in the dough from investments, but then Uncle Sam comes knocking for a piece of the pie.
That’s the NIIT in a nutshell.
The NIIT was introduced in 2010 as part of the Affordable Care Act. Its main purpose is to ensure that high-income earners pay their fair share of taxes, even on investment income. The NIIT is calculated on the lesser of your net investment income or your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) above a certain threshold.
This means that if your investment income is substantial, you might owe an extra tax on top of your regular income tax.
Who is Subject to the NIIT?

The Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) applies to certain individuals whose income exceeds specific thresholds. This tax targets individuals who earn substantial investment income, aiming to ensure fairness and prevent high-income earners from avoiding taxes on their investment gains.
The world is changing, and businesses need to adapt. Sustainability is no longer a nice-to-have, it’s a must-have. Companies are realizing this and integrating sustainability into their strategies in innovative ways. Learn how companies are making a difference in this article on the evolving landscape of corporate sustainability.
Income Thresholds for the NIIT
The NIIT is triggered when an individual’s modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) surpasses a certain threshold. The MAGI is a modified version of the adjusted gross income (AGI), which includes specific adjustments for certain income and expenses. The MAGI thresholds for the NIIT are as follows:
- For single filers, married individuals filing separately, and head of household filers, the threshold is $200,000.
- For married couples filing jointly and qualifying widow(er)s, the threshold is $250,000.
These thresholds are adjusted annually for inflation.
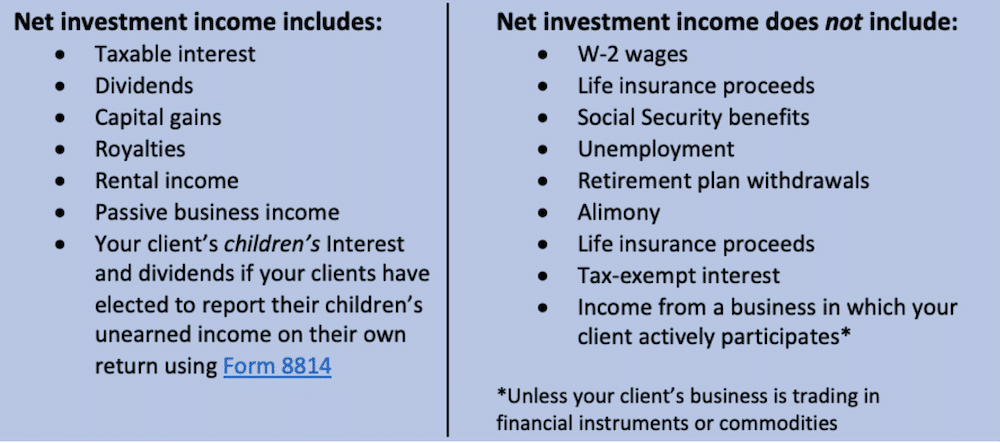
Types of Income Subject to the NIIT, What is the Net Investment Income Tax? Definition, Purpose, and Scope
The NIIT applies to a range of income derived from investments, commonly referred to as “net investment income.” This includes various types of income, such as:
- Interest income from savings accounts, bonds, and other debt instruments.
- Dividends from stocks and mutual funds.
- Capital gains from the sale of investments, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate.
- Rental income from real estate properties.
- Royalties from intellectual property, such as patents or copyrights.
- Income from certain trusts and estates.
It’s important to note that not all investment income is subject to the NIIT. For example, income from certain retirement accounts, such as traditional IRAs and 401(k)s, is generally exempt from the NIIT.
How is the NIIT Calculated?
The Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) is calculated on the lesser of two amounts: 3.8% of your net investment income or 3.8% of your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) exceeding certain thresholds. To understand how the NIIT is calculated, we’ll go through a step-by-step process using a hypothetical example.
Calculating the NIIT
The NIIT is calculated in two steps:
1. Determine your net investment income
In today’s world, businesses can’t operate in a vacuum. Stakeholder engagement is crucial for long-term success. The DealBook Summit 2024 will explore the importance of stakeholder engagement and how companies can build trust and collaboration with their stakeholders. Learn more about the power of stakeholder engagement at the DealBook Summit 2024.
This includes taxable income from investments such as dividends, interest, capital gains, and rental income.
2. Calculate the NIIT liability
The NIIT is 3.8% of the lesser of your net investment income or the amount of your MAGI exceeding the threshold.Here is a hypothetical example to illustrate the calculation: Hypothetical Example:* Net Investment Income:$50,000
Corporate social responsibility is no longer a buzzword, it’s a necessity. Companies are actively seeking ways to make a positive impact on society. The DealBook Summit 2024 will showcase inspiring case studies of companies that are leading the way in corporate social responsibility.
Learn from the best in this article.
MAGI
$150,000
Climate change is a global issue, and businesses have a crucial role to play in combating it. The DealBook Summit 2024 will bring together leading experts to discuss how businesses can be part of the solution. Learn more about the critical role of business in tackling climate change at the DealBook Summit 2024.
Threshold
$250,000 (for married filing jointly) Step 1: Determine your net investment income.In this example, the net investment income is $50,000. Step 2: Calculate the NIIT liability.
Method 1
3.8% of net investment income = 0.038$50,000 = $1,900
-
Method 2
3.8% of (MAGI
- Threshold) = 0.038
- ($150,000
- $250,000) =
- $3800 (since the result is negative, we use Method 1)
Therefore, the NIIT liability in this example is $1,900.
Relationship to Other Taxes
The NIIT is a separate tax from your regular income tax. It is calculated after your regular income tax liability is determined. However, the NIIT can affect your overall tax burden. For example, if you have a high net investment income, the NIIT can increase your total tax liability.
Deductions and Credits
There are no specific deductions or credits available for the NIIT. However, deductions and credits that reduce your MAGI can also reduce your NIIT liability. This is because the NIIT is calculated based on your MAGI, and deductions and credits can lower your MAGI.For example, if you have a large deductible expense, such as a medical expense deduction, this will reduce your MAGI and potentially lower your NIIT liability.
The NIIT and its Future
The Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) has been a part of the US tax code since 2013. While it was initially introduced as a temporary measure, its impact on high-income earners and the broader financial landscape has sparked discussions about its long-term viability and potential modifications.
Investing for impact allows you to make a difference while growing your wealth. This article explores how you can generate financial returns while also contributing to social good. Discover the world of impact investing and learn how to align your investments with your values in this article.
This section explores the potential future of the NIIT, considering arguments for and against its adjustments, and examines its effectiveness in achieving its intended goals.
Potential Changes to the NIIT
The NIIT’s future is subject to ongoing policy debates and potential changes. Some of the key areas of discussion include:
- Expansion of the NIIT’s Scope: One potential change is expanding the scope of the NIIT to encompass a broader range of investment income, potentially including capital gains from the sale of assets held for less than a year. This could raise additional revenue for the government but could also impact investors and potentially discourage long-term investment.
- Adjustment of the Threshold Income Level: Another potential change involves adjusting the threshold income level at which the NIIT applies. Raising this threshold would reduce the number of taxpayers subject to the NIIT, but it would also reduce the tax revenue generated. Lowering the threshold would increase the number of taxpayers subject to the NIIT but could raise concerns about fairness and equity.
- Modification of the Tax Rate: The current NIIT rate of 3.8% could be subject to adjustments. Increasing the rate would generate more tax revenue but could discourage investment and potentially impact economic growth. Decreasing the rate would have the opposite effect but could reduce government revenue.
Understanding the Net Investment Income Tax is crucial for investors. This comprehensive guide provides all the information you need to navigate the complexities of this tax in 2024. Learn more about the Net Investment Income Tax and how it affects your investments in this article.
Arguments for and Against Modifying the NIIT
The debate surrounding the NIIT often centers on its impact on economic growth, fairness, and the effectiveness of achieving its intended goals.
Navigating the complex world of taxes can be daunting, especially with the Net Investment Income Tax. But understanding this tax is crucial for investors. This comprehensive guide provides all the information you need to navigate the complexities of the Net Investment Income Tax in 2024.
Get a clear understanding of this tax in this article.
Arguments for Modifying the NIIT
- Stimulating Economic Growth: Some argue that reducing or eliminating the NIIT could encourage investment and stimulate economic growth. By reducing the tax burden on investment income, investors might be more inclined to allocate capital towards businesses and projects, potentially leading to increased economic activity.
The future of business is sustainable, and the trends are clear. From circular economy models to ethical sourcing, companies are embracing sustainable practices. This article delves into the key trends shaping the future of sustainable business and provides insights into what to expect in the years to come.
Discover the future of sustainable business in this insightful article.
- Promoting Fairness: Others argue that the NIIT disproportionately impacts certain income groups and could be considered unfair. They suggest that the threshold income level could be adjusted to ensure a more equitable distribution of the tax burden. Additionally, they may propose exemptions for specific types of investment income, such as retirement savings or investments in small businesses.
- Addressing Concerns about Tax Avoidance: The NIIT was initially intended to address concerns about high-income earners using loopholes to avoid paying taxes on investment income. However, some argue that the NIIT has not effectively achieved this goal and that other measures, such as stricter reporting requirements or penalties for tax evasion, might be more effective.
Arguments Against Modifying the NIIT
- Maintaining Revenue Sources: Opponents of modifying the NIIT argue that it is a valuable source of revenue for the government, particularly in times of budget deficits. Reducing or eliminating the NIIT would require finding alternative sources of revenue, which could potentially lead to higher taxes elsewhere.
- Addressing Income Inequality: Supporters of the NIIT argue that it helps to address income inequality by ensuring that high-income earners contribute their fair share of taxes. They believe that the NIIT plays a role in redistributing wealth and ensuring that the tax system is more equitable.
- Encouraging Responsible Investment: Some argue that the NIIT encourages responsible investment by discouraging speculation and promoting long-term investments. By imposing a tax on investment income, it may incentivize investors to consider the long-term implications of their investment decisions and focus on sustainable growth.
Personal Perspective on the NIIT
The NIIT is a complex tax policy with both positive and negative aspects. From a personal perspective, I believe that the NIIT has played a role in addressing income inequality and ensuring that high-income earners contribute their fair share of taxes.
However, I also recognize the potential economic and social implications of the NIIT, and I believe that ongoing discussions and adjustments to the tax policy are necessary to ensure its fairness and effectiveness.
Final Summary
The NIIT is a complex tax that can impact your investment strategy. Understanding how it works is crucial for high-income earners who want to minimize their tax liability. While the NIIT might seem like a burden, it’s important to remember that it’s designed to ensure fairness in the tax system.
By understanding the rules and potential strategies, you can navigate the NIIT effectively and make informed decisions about your investments.
Common Queries: What Is The Net Investment Income Tax? Definition, Purpose, And Scope
What are some examples of “net investment income” for NIIT purposes?
Net investment income includes things like interest, dividends, capital gains, and rental income. It doesn’t include income from your job or business.
How does the NIIT differ from other taxes on investments?
The NIIT is different from other taxes on investments because it’s an additional tax on top of your regular income tax. It’s also a flat tax rate of 3.8%, which is separate from your regular income tax bracket.
What are some strategies for minimizing or avoiding the NIIT?
Some strategies for minimizing the NIIT include investing in tax-efficient accounts like Roth IRAs or 401(k)s, diversifying your investment portfolio, and taking advantage of tax deductions and credits.