Understanding the Net Investment Income Tax in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide, this guide will help you navigate the complexities of this tax and make informed decisions about your investments. The Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) is a 3.8% tax on certain types of investment income for individuals and entities with high incomes.
It was introduced in 2013 as part of the Affordable Care Act and has since become an important consideration for investors, especially those with substantial investment portfolios.
This guide will cover everything you need to know about the NIIT, from its purpose and history to its calculation, exemptions, and reporting requirements. We will also discuss strategies for minimizing your NIIT liability and how this tax impacts investment decisions.
Whether you are a seasoned investor or just starting out, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and insights necessary to navigate the NIIT landscape effectively.
Calculating the NIIT
The Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) is a 3.8% tax levied on certain investment income exceeding specific thresholds. To determine your NIIT liability, you need to calculate the tax on your net investment income.
Calculating the NIIT
The NIIT is calculated as 3.8% of your net investment income. This income includes various sources, such as:
- Interest and dividends from investments
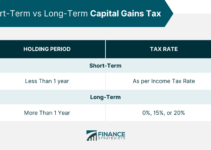
- Capital gains from the sale of assets
- Royalties
- Rental income from real estate
- Income from certain trusts and estates
However, not all investment income is subject to the NIIT. The tax only applies to income exceeding specific thresholds, which vary based on your filing status:
- Single filers: $200,000
- Married filing jointly: $250,000
- Head of household: $200,000
- Qualifying widow(er): $250,000
- Married filing separately: $125,000
To calculate your NIIT liability, you first need to determine your net investment income. This is calculated by subtracting your investment expenses from your investment income.
The DealBook Summit 2024: The Rise of ESG Investing highlighted the growing prominence of ESG considerations in investment decisions. This trend is driven by a confluence of factors, including increasing investor awareness of environmental and social issues, regulatory pressure, and the growing recognition that sustainable practices can lead to long-term financial success.
Net Investment Income = Investment Income
Investment Expenses
The DealBook Summit 2024: The Role of Business in Combating Climate Change underscored the critical role that businesses play in mitigating climate change. By adopting innovative technologies, reducing emissions, and investing in renewable energy, businesses can contribute to a more sustainable future.
This collective action is essential to addressing the global climate crisis and achieving a just transition to a low-carbon economy.
Investment expenses include things like brokerage fees, management fees, and interest paid on loans used to purchase investments.Once you have determined your net investment income, you can calculate the NIIT by multiplying it by 3.8%.
The concept of “impact investing,” as explored in the Investing for Impact: Generating Financial Returns and Social Good article, seeks to generate both financial returns and positive social and environmental impact. This approach recognizes that investments can be made in companies and projects that address pressing societal challenges while also delivering financial returns to investors.
NIIT = Net Investment Income x 0.038
Companies are increasingly integrating sustainability into their core business strategies, as evidenced in the How Companies are Integrating Sustainability into their Strategies article. This integration encompasses various aspects, including reducing environmental footprint, promoting ethical labor practices, and engaging in responsible sourcing.
By embedding sustainability into their operations, companies can enhance their reputation, attract talent, and gain a competitive advantage.
NIIT Calculation Examples
Here are a few examples of how the NIIT is calculated in different scenarios:
- Example 1:A single filer with $250,000 in investment income and $10,000 in investment expenses.
- Net investment income = $250,000 – $10,000 = $240,000
- NIIT = $240,000 x 0.038 = $9,120
- Example 2:A married couple filing jointly with $300,000 in investment income and $20,000 in investment expenses.
- Net investment income = $300,000 – $20,000 = $280,000
- NIIT = $280,000 x 0.038 = $10,640
Understanding Net Investment Income
The Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) is a tax levied on certain investment income, impacting individuals and families with substantial investment earnings. This guide delves into the intricacies of the NIIT, providing a comprehensive understanding of its application and calculation.
The The Future of Sustainable Business: Trends and Predictions article highlights emerging trends in sustainable business, including the growing demand for circular economy models, the rise of sustainable finance, and the increasing importance of data and technology in driving sustainability initiatives.
These trends suggest that sustainable business practices will continue to evolve and become even more central to business success in the future.
This section focuses on the definition of “net investment income,” explaining its components and identifying income types that fall under its scope.
Defining Net Investment Income, Understanding the Net Investment Income Tax in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide
The Internal Revenue Code defines “net investment income” as the excess of investment income over investment expenses. This income is subject to the NIIT, a 3.8% tax on top of other applicable taxes. Understanding the components of net investment income is crucial for determining its applicability to an individual’s tax situation.
A key challenge in the field of ESG investing is the lack of standardized metrics for measuring ESG performance. The Measuring ESG Performance: Standards and Frameworks article discusses the various frameworks and standards being developed to address this issue. These frameworks aim to provide a common language and methodology for evaluating ESG performance, enabling investors to make more informed decisions.
Components of Net Investment Income
Net investment income is calculated by subtracting investment expenses from investment income. The following components contribute to its calculation:
- Investment Income:This includes various income sources, such as dividends, interest, capital gains, and rental income.
- Investment Expenses:These are costs directly related to generating investment income, including expenses for managing investments, trading commissions, and depreciation of investment property.
To illustrate, imagine an individual earning $10,000 in dividends and $5,000 in interest income. If their investment expenses for the year amount to $2,000, their net investment income would be calculated as follows:
Net Investment Income = ($10,000 + $5,000)- $2,000 = $13,000
The DealBook Summit 2024: The Importance of Stakeholder Engagement emphasized the crucial role of stakeholder engagement in driving sustainable business practices. Engaging with stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities, is essential for understanding their concerns and expectations, and for building trust and transparency.
This approach helps companies align their business strategies with the needs and values of their stakeholders.
Common Types of Investment Income Subject to NIIT
The NIIT applies to various types of investment income. Some of the most common examples include:
- Dividends:These are distributions of profits paid by corporations to their shareholders.
- Interest:Income earned from lending money, such as through bonds, savings accounts, or certificates of deposit.
- Capital Gains:Profits realized from selling assets like stocks, bonds, or real estate for a higher price than the purchase price.
- Rental Income:Income earned from renting out property, such as apartments, houses, or commercial spaces.
Income Excluded from Net Investment Income
While numerous income types fall under the NIIT, some are explicitly excluded. These include:
- Wages and Salaries:Income earned from employment, where an individual receives a salary or hourly wage.
- Self-Employment Income:Income earned from running a business or engaging in a trade or profession.
- Income from Certain Retirement Accounts:Income from traditional IRAs, 401(k)s, and Roth IRAs is generally not subject to the NIIT.
These exclusions are based on the principle that the NIIT should target investment income, not income derived from active labor or retirement savings.
Explanation of the NIIT for a Layperson
The NIIT is an additional tax imposed on certain investment income. It is a 3.8% tax levied on top of other applicable taxes, such as income tax. This tax applies when an individual’s modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) exceeds a certain threshold.
For 2024, the threshold is $250,000 for single filers and $500,000 for married couples filing jointly.
For example, consider a single filer with a MAGI of $300,000 and $20,000 in net investment income. Since their MAGI exceeds the threshold, they would be subject to the NIIT. The NIIT on their investment income would be calculated as follows:
NIIT = $20,000 x 3.8% = $760
This $760 would be added to their overall tax liability, making the NIIT a significant factor for individuals with substantial investment income and high MAGIs.
Closing Notes: Understanding The Net Investment Income Tax In 2024: A Comprehensive Guide

As you have seen, the Net Investment Income Tax is a complex but important aspect of tax planning for many individuals and entities. By understanding the intricacies of this tax, you can make informed investment decisions and minimize your tax liability.
Remember, this guide provides general information and should not be considered financial advice. It is always best to consult with a qualified tax professional for personalized guidance and to ensure compliance with all applicable tax laws.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT)?
The NIIT was implemented as part of the Affordable Care Act to generate revenue for the healthcare system. It is a tax on investment income for individuals and entities with high incomes.
Is there a specific form for filing the NIIT?
Yes, you will need to file Form 8960, Net Investment Income Tax, to report and pay the NIIT. The specific form you use may vary depending on your tax filing status and the type of entity you are.
How does the NIIT affect my investment decisions?
The NIIT can impact your investment decisions by influencing your risk appetite, investment horizon, and asset allocation. It may lead you to consider tax-efficient investments or adjust the timing of your investment transactions.
Are there any exemptions from the NIIT?
Yes, there are certain exemptions and deductions available for the NIIT. These can include exemptions for specific types of income, such as income from certain retirement accounts, or deductions for certain expenses related to investments.