Types of Inflation: Demand-Pull vs. Cost-Push in November 2024 sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Inflation, the persistent rise in the general price level of goods and services, is a complex economic phenomenon with far-reaching consequences.
Understanding its different forms is crucial for navigating the economic landscape and making informed decisions.
Obtain access to CPI and the November 2024 Election to private resources that are additional.
This analysis delves into the two primary types of inflation: demand-pull and cost-push. Demand-pull inflation occurs when aggregate demand outpaces the economy’s ability to produce goods and services, leading to upward pressure on prices. Conversely, cost-push inflation arises from increased production costs, such as higher wages or raw material prices, which businesses pass on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
Obtain access to CPI and the Service Sector in November 2024 to private resources that are additional.
We’ll explore the drivers, consequences, and potential solutions for each type of inflation, focusing on their potential impact in November 2024.
Introduction to Inflation: Types Of Inflation: Demand-Pull Vs. Cost-Push In November 2024
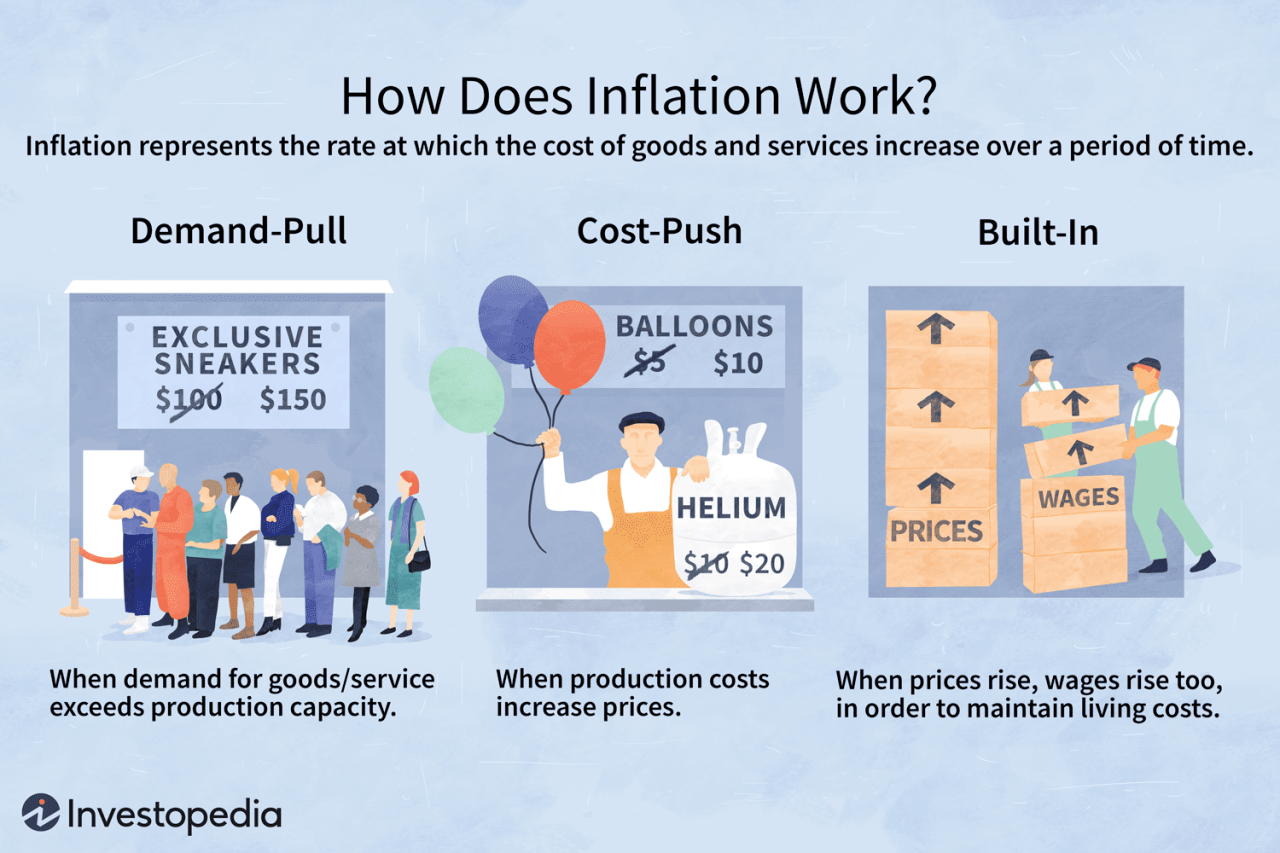
Inflation is a persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. It erodes the purchasing power of money, meaning that you can buy fewer goods and services with the same amount of money as before.
Understanding inflation is crucial because it impacts various aspects of the economy, including consumer spending, business investment, and government policies.
Notice Data Collection Methods for the November 2024 CPI for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Inflation can be broadly categorized into two main types: demand-pull inflation and cost-push inflation. Each type has its own underlying causes, mechanisms, and consequences.
Further details about The Future of the CPI: What to Expect After November 2024 is accessible to provide you additional insights.
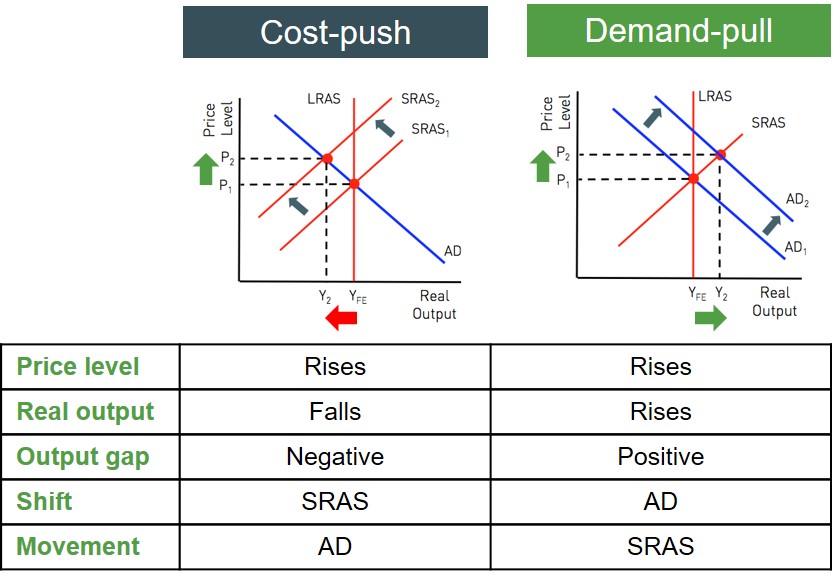
Demand-Pull Inflation
Demand-pull inflation occurs when there is an increase in aggregate demand, which is the total demand for goods and services in an economy, outpacing the supply of those goods and services. This imbalance between supply and demand leads to higher prices.
In November 2024, several factors could contribute to demand-pull inflation, including:
- Strong consumer confidence and spending:If consumers feel optimistic about the economy and their own financial situation, they may be more likely to spend, leading to increased demand.
- Government spending:Increased government spending on infrastructure, social programs, or other initiatives can stimulate demand and potentially lead to inflation.
- Low interest rates:When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging businesses and consumers to invest and spend, which can boost demand.
The consequences of demand-pull inflation can be both positive and negative. On the positive side, it can signal a healthy economy with strong growth and job creation. However, if inflation becomes excessive, it can lead to:
- Reduced purchasing power:As prices rise, consumers have less purchasing power, leading to a decline in living standards.
- Uncertainty and instability:High inflation can create uncertainty for businesses and consumers, making it difficult to plan for the future and potentially hindering investment.
- Distorted economic signals:Inflation can distort the signals that prices send to producers and consumers, making it difficult to allocate resources efficiently.
Cost-Push Inflation, Types of Inflation: Demand-Pull vs. Cost-Push in November 2024
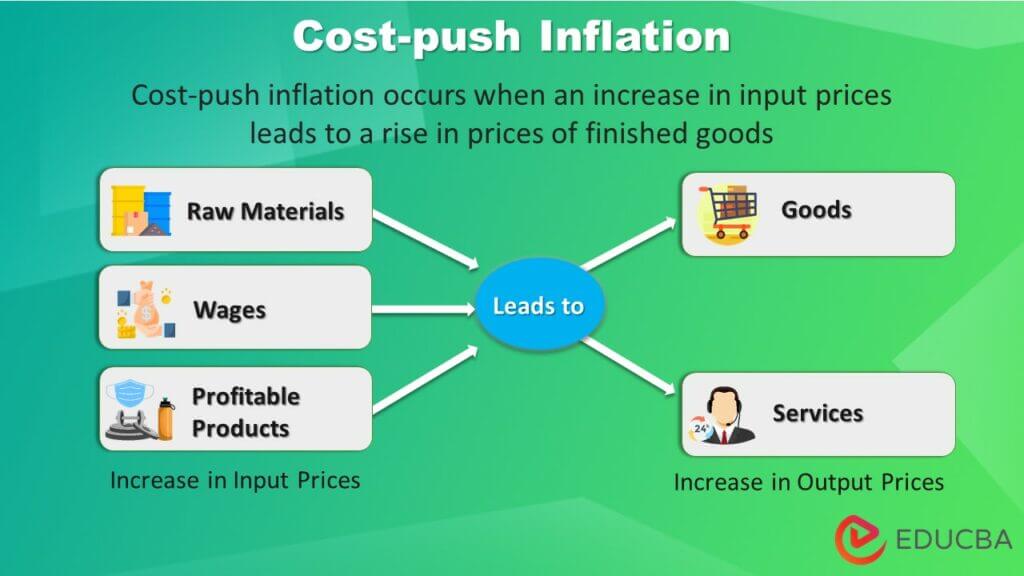
Cost-push inflation occurs when the cost of producing goods and services increases, leading to higher prices. This can happen due to factors such as rising input costs, supply chain disruptions, or increased labor costs.
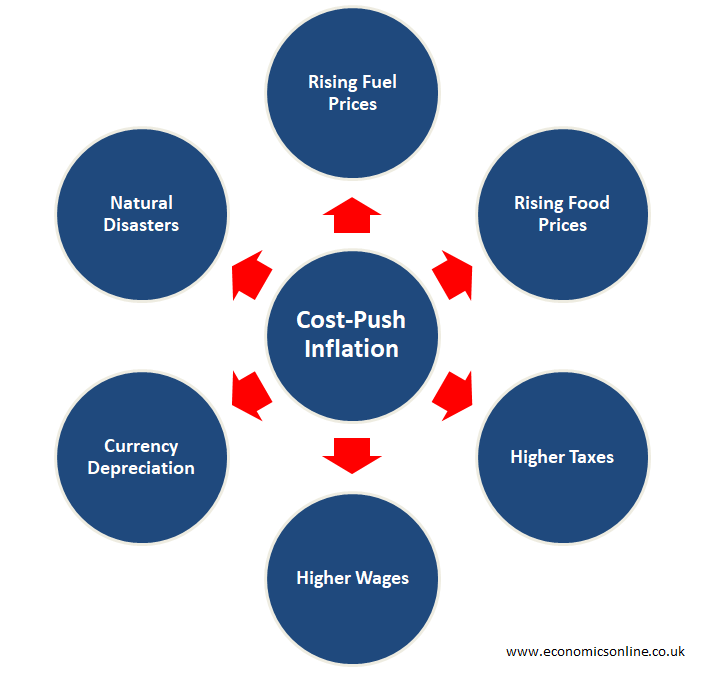
In November 2024, several factors could contribute to cost-push inflation, including:
- Higher energy prices:Rising energy prices, such as oil and gas, can increase the cost of production for many industries.
- Supply chain disruptions:Ongoing supply chain issues, potentially exacerbated by geopolitical events or natural disasters, can lead to shortages and higher prices for certain goods.
- Increased labor costs:Labor shortages or wage increases can push up the cost of production for businesses, leading to higher prices.
The consequences of cost-push inflation are generally negative for the economy. It can lead to:
- Reduced economic output:As production costs rise, businesses may reduce output or raise prices, leading to a slowdown in economic growth.
- Job losses:If businesses are unable to pass on higher costs to consumers, they may have to reduce their workforce, leading to job losses.
- Reduced competitiveness:Higher prices can make domestic goods less competitive in international markets, potentially leading to a decline in exports.
Comparing Demand-Pull and Cost-Push Inflation
Demand-pull and cost-push inflation are distinct but can sometimes occur simultaneously, making it challenging to identify and address the root causes. Understanding the key differences between these types of inflation is essential for policymakers and businesses.
Obtain a comprehensive document about the application of The Impact of Technology on the November 2024 CPI that is effective.
| Characteristic | Demand-Pull Inflation | Cost-Push Inflation |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Increased aggregate demand | Increased production costs |
| Mechanism | Excess demand outpaces supply, leading to higher prices | Higher input costs are passed on to consumers, leading to higher prices |
| Examples | Strong consumer spending, government spending, low interest rates | Rising energy prices, supply chain disruptions, increased labor costs |
| Potential Solutions | Fiscal and monetary policies to reduce demand, such as increased taxes or higher interest rates | Policies to address supply chain disruptions, control input costs, or reduce labor shortages |
Inflation in November 2024
The economic landscape in November 2024 is likely to be influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including global geopolitical events, supply chain dynamics, and consumer behavior. To assess the potential for inflation, policymakers and economists will monitor key indicators such as:
- Price indices:The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) measure changes in the prices of goods and services consumed by households and businesses, respectively. These indices provide insights into the overall inflation rate and its impact on different sectors.
- Consumer spending patterns:Changes in consumer spending patterns, such as increased demand for certain goods or services, can indicate underlying inflationary pressures.
- Wage growth:Rising wages can contribute to both demand-pull and cost-push inflation. Monitoring wage growth is crucial for understanding the potential impact on prices.
Inflation in November 2024 could have a significant impact on various sectors of the economy, including:
- Consumer goods and services:Inflation can lead to higher prices for everyday goods and services, eroding consumer purchasing power and potentially impacting consumption patterns.
- Manufacturing and production:Rising input costs, such as energy and raw materials, can affect manufacturing costs and profitability, potentially leading to price increases or reduced output.
- Financial markets:Inflation can impact interest rates, asset prices, and the value of investments, potentially creating volatility and uncertainty in financial markets.
Strategies for Managing Inflation
Managing inflation is a key objective of economic policy. Policymakers use a combination of monetary and fiscal policies to influence aggregate demand and control inflation.
Discover the crucial elements that make CPI and the Treatment of New Products in November 2024 the top choice.
Monetary policy, implemented by central banks, focuses on controlling the money supply and interest rates. Tools include:
- Interest rate adjustments:Raising interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, reducing consumer and business spending and curbing demand-pull inflation. Conversely, lowering interest rates can stimulate economic activity.
- Quantitative easing:This involves injecting liquidity into the financial system by purchasing assets, such as government bonds, to lower interest rates and stimulate economic activity.
Fiscal policy, implemented by governments, involves adjusting government spending and taxation to influence aggregate demand. Tools include:
- Government spending:Increasing government spending can stimulate demand and potentially lead to inflation. Conversely, reducing government spending can help curb inflation.
- Taxation:Increasing taxes can reduce disposable income and spending, helping to control demand-pull inflation. Conversely, reducing taxes can stimulate economic activity.
The effectiveness of different policy interventions in addressing demand-pull and cost-push inflation depends on the specific economic conditions. For example, monetary policy may be more effective in addressing demand-pull inflation, while fiscal policy may be more effective in addressing cost-push inflation caused by supply chain disruptions.
Find out about how CPI and Housing Affordability in November 2024 can deliver the best answers for your issues.
Policymakers must also consider the potential trade-offs associated with different inflation management strategies. For example, raising interest rates to curb inflation can slow economic growth and potentially lead to job losses. Conversely, reducing taxes to stimulate economic activity can lead to higher government debt.
Ultimate Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of demand-pull and cost-push inflation in November 2024, it’s clear that understanding these distinct forces is essential for policymakers and individuals alike. By recognizing the underlying causes and potential consequences of each type of inflation, we can better navigate the economic landscape and make informed decisions to mitigate its potential negative impacts.
Whether it’s through appropriate monetary and fiscal policies, or by understanding consumer behavior and adapting spending patterns, proactive measures can help maintain economic stability and promote sustainable growth.
Key Questions Answered
What are the key differences between demand-pull and cost-push inflation?
Demand-pull inflation is driven by increased demand, while cost-push inflation is caused by rising production costs. Demand-pull inflation is often associated with economic growth, while cost-push inflation can lead to stagflation (high inflation and slow economic growth).
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of How the November 2024 CPI Affects Your Daily Life.
How does inflation impact different sectors of the economy?
When investigating detailed guidance, check out CPI and the Changing Consumer Landscape in November 2024 now.
Inflation can have varying impacts on different sectors. For example, sectors heavily reliant on raw materials may experience higher costs, while sectors with strong demand might see increased profits. The impact also depends on the specific type of inflation.
What are some potential solutions for managing inflation?
Find out further about the benefits of The CPI and the Environment in November 2024 that can provide significant benefits.
Strategies for managing inflation include monetary policy (adjusting interest rates) and fiscal policy (government spending and taxation). The effectiveness of these policies depends on the type of inflation and the specific economic context.