Is Annuity Income Capital Gains 2024? This question is at the forefront of many minds as individuals seek to understand the tax implications of their retirement income. Annuities, often considered a cornerstone of retirement planning, offer a stream of guaranteed income, but their tax treatment can be complex.
This guide delves into the intricacies of how annuity income is taxed, particularly in relation to capital gains, providing valuable insights for individuals navigating the complexities of retirement planning.
Understanding the tax implications of annuities is crucial for maximizing retirement income and minimizing tax liabilities. This guide will explore the various types of annuities and their respective tax treatments, shedding light on the tax implications of capital gains derived from annuity investments.
By examining the current tax laws and regulations governing annuity income in 2024, this guide will empower individuals to make informed decisions about their retirement planning strategies.
Understanding Annuities and Capital Gains
Annuities and capital gains are two distinct financial concepts that often intertwine, especially when it comes to retirement planning. Understanding the tax implications of each is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
Types of Annuities and Tax Implications
Annuities are financial products that provide a stream of income, typically for a set period or for life. They are often used as a retirement savings tool, but they can also be used to provide income for other purposes, such as supplementing Social Security or covering healthcare costs.
There are two main types of annuities:
- Fixed annuitiesoffer a guaranteed rate of return, meaning the payments you receive will be predictable. These are typically tax-deferred, meaning that you won’t pay taxes on the earnings until you begin receiving payments. However, the interest earned on a fixed annuity is taxed as ordinary income when it is withdrawn.
- Variable annuitiesoffer the potential for higher returns, but they also come with more risk. The payments you receive from a variable annuity will depend on the performance of the underlying investments. The earnings from variable annuities are taxed as capital gains when withdrawn.
Capital Gains: Definition and Taxation
Capital gains refer to the profit realized from selling an asset for more than its purchase price. The tax rate on capital gains depends on how long you’ve held the asset.
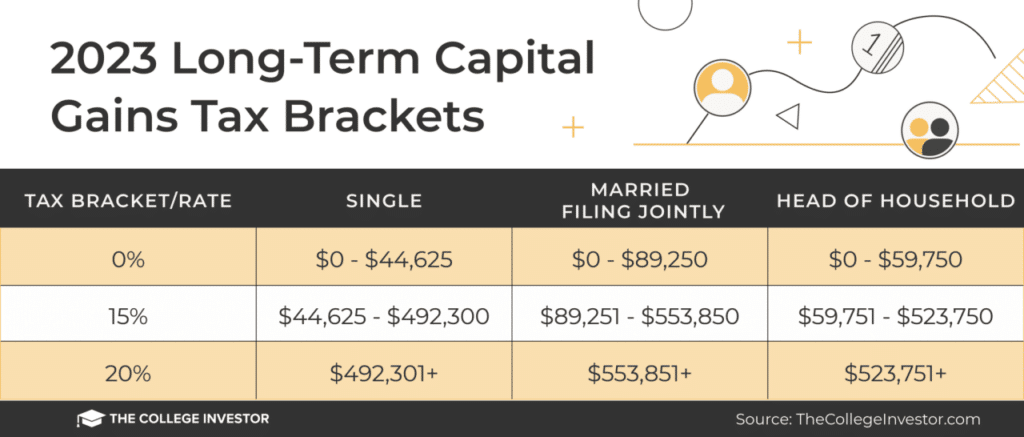
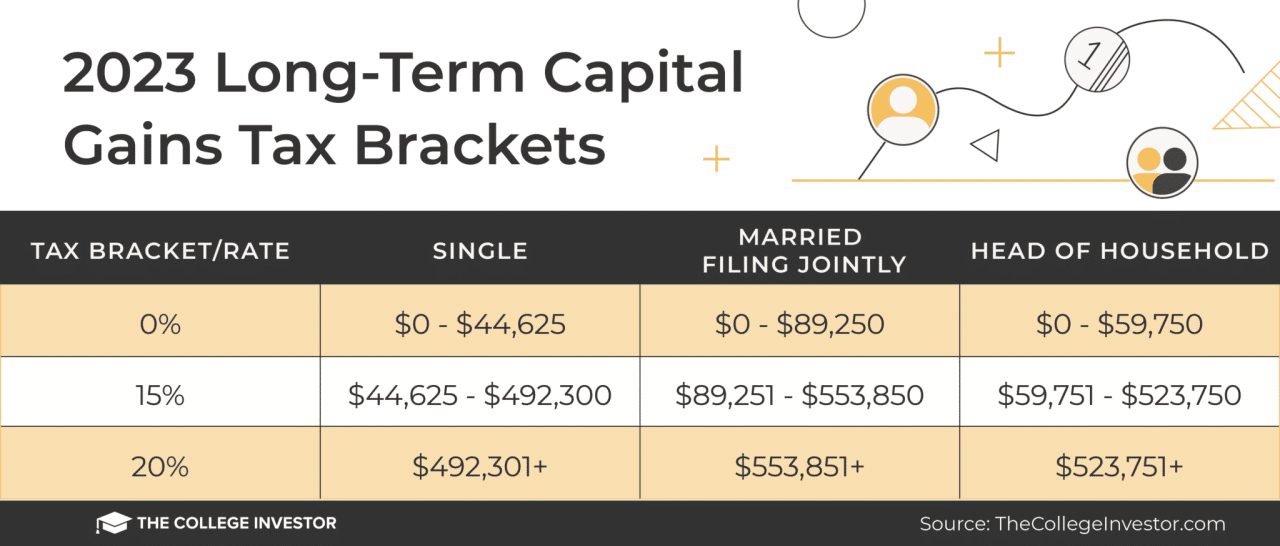
- Short-term capital gainsare taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, while long-term capital gainsare taxed at a lower rate, typically 0%, 15%, or 20% depending on your income level.
Tax Treatment of Annuity Payments vs. Other Income
Annuity payments are generally taxed as ordinary income. This means they are subject to the same tax rates as your wages, salary, and other forms of earned income. However, the tax treatment of annuity payments can vary depending on the type of annuity, the age of the annuitant, and the timing of the payments.
For example, if you receive a lump-sum payment from an annuity, it may be taxed differently than if you receive payments over time.
Annuity Income in 2024
The tax laws governing annuity income are subject to change. It is essential to stay updated on the latest regulations to ensure accurate tax planning.
Current Tax Laws and Potential Changes
As of 2024, annuity income is generally taxed as ordinary income. This means that the payments you receive from an annuity are subject to the same tax rates as your wages, salary, and other forms of earned income. However, there are some exceptions to this rule, such as the exclusion of certain types of annuity payments from income for individuals who are disabled or have reached a certain age.
It is crucial to stay informed about potential changes to tax laws regarding annuity income. These changes could impact the tax treatment of your annuity payments, potentially leading to adjustments in your tax liability. Consulting with a tax professional can help you navigate these complexities and ensure compliance with the latest regulations.
Examples of Annuity Income Taxation
Here are some examples of how annuity income is taxed in different scenarios:
- Scenario 1:A 65-year-old individual receives monthly payments from a fixed annuity. These payments are taxed as ordinary income, and the individual’s tax liability will depend on their overall income level.
- Scenario 2:A 70-year-old individual receives a lump-sum payment from a variable annuity. This payment is taxed as capital gains, and the individual’s tax liability will depend on the holding period of the investment and their income level.
Taxation of Annuity Distributions
The tax treatment of annuity distributions depends on several factors, including the type of annuity, the timing of the distributions, and the age of the annuitant.
Tax Treatment of Fixed and Variable Annuity Distributions
The tax treatment of fixed and variable annuity distributions differs mainly in how the earnings are taxed.
- Fixed annuity distributionsare taxed as ordinary income. This means that the payments you receive from a fixed annuity are subject to the same tax rates as your wages, salary, and other forms of earned income. The interest earned on a fixed annuity is taxed as ordinary income when it is withdrawn.
- Variable annuity distributionsare taxed as capital gains. This means that the payments you receive from a variable annuity are taxed at a lower rate than ordinary income, typically 0%, 15%, or 20% depending on your income level. However, the earnings from variable annuities are taxed as capital gains when withdrawn.
Tax Implications of Lump-Sum vs. Installment Payments
The tax implications of receiving annuity payments as a lump sum versus installments can vary significantly.
| Payment Type | Tax Implications |
|---|---|
| Lump-Sum | The entire amount of the lump-sum payment is taxed as ordinary income or capital gains, depending on the type of annuity. This can result in a significant tax liability in the year the payment is received. |
| Installments | Each installment payment is taxed as ordinary income or capital gains, depending on the type of annuity. This can spread out the tax liability over a longer period, potentially reducing the overall tax burden. |
Tax Consequences of Early Withdrawal
Withdrawing from an annuity before the annuitization period, the period when you begin receiving payments, can have significant tax consequences.
- You may be subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty, in addition to ordinary income tax or capital gains tax, depending on the type of annuity.
- There may also be surrender charges, which are fees imposed by the insurance company for withdrawing from the annuity before a certain period. These fees can vary depending on the annuity contract and the length of time the annuity has been held.
Annuity Income and Capital Gains
While annuity income is generally taxed as ordinary income, there are situations where capital gains may be realized when withdrawing from an annuity.
Potential for Capital Gains
Capital gains can arise from annuity investments when the underlying investments in a variable annuity appreciate in value. When you withdraw from a variable annuity, the portion of the withdrawal that represents the growth in the investment is taxed as a capital gain.
This can be a complex calculation, and it’s important to consult with a financial advisor to understand the tax implications of your specific situation.
Tax Implications of Capital Gains from Annuities
The tax implications of capital gains derived from annuity investments depend on the holding period of the investment. Short-term capital gains, realized from investments held for less than a year, are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. Long-term capital gains, realized from investments held for a year or more, are taxed at a lower rate, typically 0%, 15%, or 20% depending on your income level.
Flowchart Illustrating Tax Treatment
The following flowchart illustrates the tax treatment of annuity income and capital gains:
[Flowchart illustrating the tax treatment of annuity income and capital gains. Include key decisions points, such as type of annuity, holding period, and withdrawal timing, and corresponding tax implications. The flowchart should be detailed and informative, providing a clear visual representation of the tax implications.]
Tax Planning Strategies for Annuities
Tax planning for annuities can help you minimize your tax liability and maximize your retirement income.
Strategies to Minimize Tax Liability, Is Annuity Income Capital Gains 2024
Here are some strategies to minimize your tax liability on annuity income:
- Consider a Roth IRA or Roth 401(k): Contributions to Roth IRAs and Roth 401(k)s are made with after-tax dollars, but qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free. This can be a more tax-efficient option than traditional IRAs and 401(k)s, which are funded with pre-tax dollars and subject to taxation in retirement.
- Delay annuitization: If possible, delay annuitizing your annuity until you are in a lower tax bracket. This can help reduce your tax liability on the payments you receive.
- Use tax-loss harvesting: If you have losses on other investments, you can use tax-loss harvesting to offset capital gains from your annuity investments. This can help reduce your overall tax liability.
Tax Deductions and Credits
There are some tax deductions and credits that may apply to annuity payments, such as:
- Medical expense deduction: You may be able to deduct medical expenses that exceed a certain percentage of your adjusted gross income, including premiums paid for long-term care insurance, which can be used to fund an annuity.
- Retirement savings contributions credit: You may be eligible for a tax credit for contributions to a Roth IRA or Roth 401(k), depending on your income level.
Structuring Annuity Investments for Tax Efficiency
The way you structure your annuity investments can have a significant impact on your tax liability. Here are some tips for structuring annuity investments for optimal tax efficiency:
- Consider a combination of fixed and variable annuities: This can help diversify your portfolio and potentially reduce your overall tax liability.
- Use a tax-advantaged account: If you have a traditional IRA or 401(k), you can use it to purchase an annuity. This can help reduce your tax liability on the earnings from the annuity.
- Consult with a financial advisor: A financial advisor can help you develop a tax-efficient strategy for your annuity investments.
End of Discussion
Navigating the tax landscape of annuity income can be challenging, but by understanding the nuances of capital gains and tax regulations, individuals can optimize their retirement planning strategies. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the tax treatment of annuity income in 2024, equipping readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their retirement investments.
By carefully considering the tax implications of annuity distributions and capital gains, individuals can maximize their retirement income and minimize their tax liabilities, ensuring a more financially secure future.
Detailed FAQs: Is Annuity Income Capital Gains 2024
How are annuity payments taxed?
Annuity payments are generally taxed as ordinary income. The portion of each payment that represents a return of your principal investment is tax-free, while the remaining portion is taxed as ordinary income.
What is the difference between fixed and variable annuities?
Fixed annuities offer a guaranteed rate of return, while variable annuities have returns that fluctuate based on the performance of underlying investments. Both types of annuities have different tax implications, so it’s important to understand the distinctions before making a decision.
Can I withdraw from an annuity before the annuitization period?
Yes, you can withdraw from an annuity before the annuitization period, but you may be subject to penalties and taxes. It’s important to carefully consider the tax consequences before making a withdrawal.
How do I minimize my tax liability on annuity income?
There are several strategies you can employ to minimize your tax liability on annuity income, such as choosing a deferred annuity, taking advantage of tax deductions and credits, and structuring your annuity investments for optimal tax efficiency. Consulting with a tax professional can provide personalized advice.