Cryptocurrency and Blockchain: Regulation, Innovation, and Investment, a dynamic landscape that has captured the attention of investors, regulators, and technologists alike. This intersection of finance, technology, and policy presents both immense opportunities and significant challenges, shaping the future of our financial systems and beyond.
This exploration delves into the evolution of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology, examining the regulatory frameworks that are emerging to govern this nascent sector. We will explore the innovative applications of blockchain beyond finance, analyzing the potential impact on various industries and the societal implications of this decentralized paradigm.
Finally, we will consider the investment landscape, assessing opportunities and risks while providing insights into managing risk in this volatile market.
The Rise of Cryptocurrency and Blockchain
Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology have emerged as transformative forces in the global financial landscape, challenging traditional institutions and redefining the way we think about value, security, and trust. This revolution began in 2008 with the publication of a white paper by an anonymous individual known as Satoshi Nakamoto, introducing the concept of Bitcoin, the first decentralized digital currency.
Historical Development and Key Milestones
The history of cryptocurrency and blockchain is marked by a series of significant milestones and influential figures who have shaped its evolution. Bitcoin’s launch in 2009, powered by the groundbreaking blockchain technology, sparked a wave of innovation and interest in decentralized systems.
- 2008:Satoshi Nakamoto publishes the Bitcoin white paper, outlining the concept of a decentralized digital currency.
- 2009:The Bitcoin network is launched, marking the birth of the first cryptocurrency.
- 2011:Litecoin, a fork of Bitcoin, is introduced, offering faster transaction speeds.
- 2013:The price of Bitcoin experiences a surge, reaching a peak of over $1,000, attracting wider attention and investment.
- 2014:Ethereum, a platform for smart contracts and decentralized applications, is launched, expanding the possibilities of blockchain beyond just cryptocurrency.
- 2017:The cryptocurrency market experiences a boom, with the total market capitalization exceeding $1 trillion, fueled by the emergence of new cryptocurrencies and increased investment.
- 2018:The market experiences a correction, with prices declining significantly, but innovation continues, with the development of new blockchain applications and regulatory frameworks.
Underlying Principles of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology underpins the operation of cryptocurrencies and offers a secure and transparent way to record and verify transactions. Its core principles include:
- Decentralization:Blockchain networks are distributed across multiple computers, eliminating reliance on a central authority. This makes them resistant to censorship and manipulation.
- Immutability:Once a transaction is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures the integrity and permanence of the data.
- Transparency:All transactions on a blockchain are publicly accessible, providing a transparent and auditable record of activity.
Types of Cryptocurrencies
The cryptocurrency landscape is diverse, with various types of cryptocurrencies serving different purposes and utilizing different technologies. Some of the most prominent categories include:
- Bitcoin (BTC):The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, known for its decentralized nature and limited supply.
- Ethereum (ETH):A platform for smart contracts and decentralized applications, enabling the development of a wide range of blockchain-based solutions.
- Stablecoins:Cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value, typically pegged to fiat currencies like the US dollar, to mitigate price volatility.
- Privacy Coins:Cryptocurrencies that prioritize user privacy, using techniques to obscure transaction details and sender/receiver identities.
- Utility Tokens:Cryptocurrencies used to access or utilize specific services or platforms, often within a particular ecosystem.
Regulatory Landscape and Challenges
The rapid growth of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology has prompted regulators worldwide to grapple with the complexities of overseeing this decentralized and evolving sector. Governments and financial institutions are navigating the challenges of balancing innovation with consumer protection and financial stability.
Technology’s transformative power is reshaping industries and driving innovation across the board. The summit emphasized the critical role of leadership in navigating this evolving landscape. Leadership Reimagined explored the qualities necessary for effective leadership in a world defined by purpose, resilience, and the needs of the next generation.
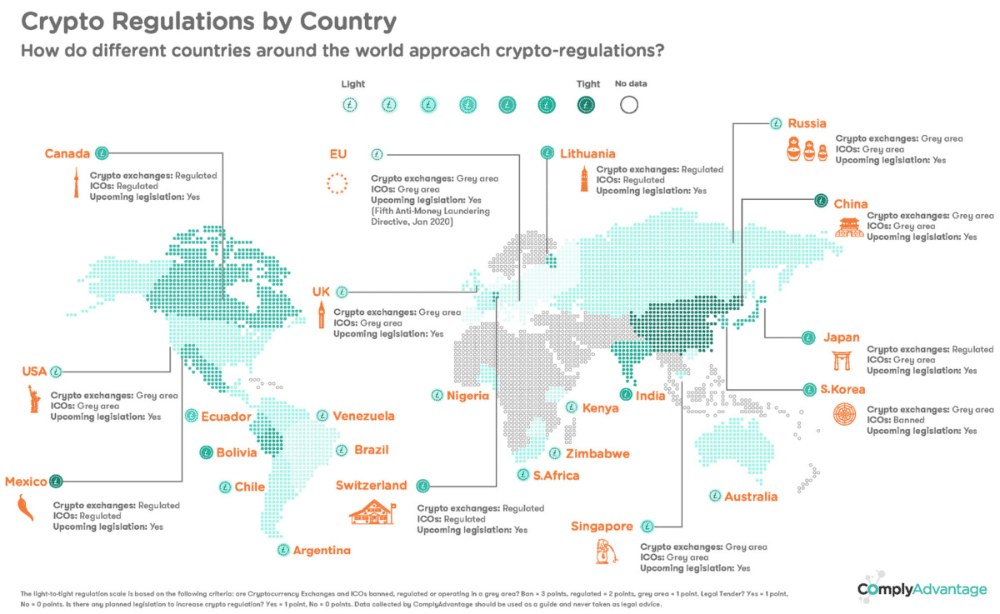
Regulatory Approaches Across Jurisdictions
Different jurisdictions have adopted diverse approaches to regulating cryptocurrency and blockchain. Some have embraced a more permissive approach, fostering innovation and attracting investment, while others have implemented stricter regulations to mitigate risks.
- United States:The US has adopted a patchwork approach, with various agencies, including the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), and the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), overseeing different aspects of the cryptocurrency industry.
- European Union:The EU has implemented the Fifth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (AMLD5), which requires cryptocurrency exchanges and wallet providers to comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations.
- China:China has taken a more restrictive approach, banning cryptocurrency exchanges and initial coin offerings (ICOs), citing concerns about market volatility and financial risks.
Challenges and Opportunities of Regulating a Decentralized Technology, Cryptocurrency and Blockchain: Regulation, Innovation, and Investment
Regulating cryptocurrency and blockchain presents unique challenges due to their decentralized nature, global reach, and rapid evolution. Some of the key challenges include:
- Defining Regulatory Boundaries:Determining which entities and activities fall under the purview of existing regulations or require new frameworks.
- Cross-Border Cooperation:Coordinating regulatory efforts across different jurisdictions to ensure consistency and prevent regulatory arbitrage.
- Technological Complexity:Understanding the intricacies of blockchain technology and its applications to effectively regulate the industry.
- Consumer Protection:Protecting investors from scams, fraud, and market manipulation.
- Financial Stability:Mitigating the potential risks of cryptocurrency volatility and its impact on the broader financial system.
Examples of Regulatory Frameworks
Several regulatory frameworks have been implemented or are under consideration to address the challenges of overseeing cryptocurrency and blockchain.
- Travel Rule:A regulatory framework aimed at improving transparency and combating money laundering by requiring financial institutions to share information about senders and receivers of cryptocurrency transactions.
- Stablecoin Regulations:Regulations focused on ensuring the stability and transparency of stablecoins, which are pegged to fiat currencies.
- Cryptocurrency Exchange Licensing:Requirements for cryptocurrency exchanges to obtain licenses to operate, demonstrating compliance with KYC, AML, and other regulations.
Innovation and Applications Beyond Finance
Beyond its use in financial markets, blockchain technology is rapidly expanding into various sectors, revolutionizing industries and creating new opportunities. Its inherent features of security, transparency, and immutability make it suitable for applications that require trust and efficiency.
Emerging Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is being used to develop innovative solutions in diverse industries, including:
- Healthcare:Securely storing and sharing patient medical records, managing supply chains for pharmaceuticals, and facilitating clinical trials.
- Supply Chain Management:Tracking the origin and movement of goods, ensuring product authenticity, and improving supply chain transparency.
- Identity Verification:Creating secure and tamper-proof digital identities, simplifying identity verification processes, and reducing fraud.
- Voting Systems:Enabling secure and transparent voting systems, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing voter confidence.
- Intellectual Property:Protecting and verifying ownership of intellectual property, preventing counterfeiting and ensuring fair compensation for creators.
Examples of Blockchain Implementation
Several real-world examples demonstrate the transformative potential of blockchain technology across different industries.
The Dealbook Summit 2024 provided insightful takeaways for investors, particularly focusing on emerging markets and the global economic outlook. The summit highlighted the potential of emerging markets, exploring both opportunities and challenges. This rise comes with new opportunities and challenges, demanding a nuanced understanding of the landscape.
- Walgreens:Using blockchain to track the distribution of prescription drugs, ensuring their authenticity and provenance.
- IBM:Developing blockchain-based solutions for supply chain management, enabling businesses to track goods from origin to destination.
- Everledger:Utilizing blockchain to create a digital registry for diamonds, combating fraud and ensuring authenticity.
Potential Impact of Blockchain on Various Sectors
Blockchain technology has the potential to disrupt and reshape various sectors, driving efficiency, transparency, and trust.
- Financial Services:Facilitating faster and cheaper cross-border payments, enabling new financial products and services, and improving financial inclusion.
- Government:Streamlining government processes, improving data security, and enhancing transparency and accountability.
- Education:Verifying academic credentials, managing student records, and creating secure and transparent learning platforms.
- Energy:Optimizing energy grids, enabling peer-to-peer energy trading, and promoting renewable energy adoption.
Investment Opportunities and Risks
The growth of cryptocurrency and blockchain has opened up new investment opportunities for individuals and institutions. However, investing in this nascent and volatile market comes with inherent risks that require careful consideration.
Investment Vehicles
Investors have various ways to participate in the cryptocurrency and blockchain market, including:
- Direct Asset Purchases:Buying and holding cryptocurrencies directly through exchanges or wallets.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs):Investing in cryptocurrency ETFs that track the performance of a basket of cryptocurrencies.
- Blockchain-Based Projects:Investing in blockchain-based projects through initial coin offerings (ICOs) or other fundraising mechanisms.
- Blockchain Companies:Investing in publicly traded companies that develop or utilize blockchain technology.
Risks Associated with Cryptocurrency Investments
Investing in cryptocurrencies carries significant risks, including:
- Volatility:Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile, subject to rapid fluctuations, and can experience significant price swings in a short period.
- Market Manipulation:The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies makes them susceptible to manipulation, with potential for price distortions and market bubbles.
- Regulatory Uncertainty:The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is still evolving, with potential for changes that could impact investment returns.
- Security Risks:Cryptocurrencies are vulnerable to hacking and theft, requiring robust security measures to protect investments.
- Lack of Fundamental Value:Unlike traditional assets like stocks or bonds, cryptocurrencies lack inherent value and their price is primarily driven by market sentiment and speculation.
Assessing Investment Opportunities and Managing Risk
Before investing in cryptocurrencies, it is crucial to conduct thorough research and understand the risks involved.
- Diversification:Spread investments across different cryptocurrencies and investment vehicles to mitigate risk.
- Due Diligence:Carefully evaluate the underlying technology, team, and business model of any blockchain project before investing.
- Risk Tolerance:Understand your own risk tolerance and invest only what you can afford to lose.
- Security Measures:Implement strong security measures to protect your cryptocurrency investments from hacking and theft.
- Long-Term Perspective:Consider a long-term investment horizon, as cryptocurrency prices can fluctuate significantly in the short term.
Societal and Ethical Considerations
The widespread adoption of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology raises important societal and ethical considerations, impacting financial inclusion, privacy, and the future of our digital world.
Impact on Financial Inclusion
Cryptocurrencies have the potential to enhance financial inclusion by providing access to financial services for individuals and communities who are traditionally underserved by traditional banking systems.
- Cross-Border Payments:Cryptocurrencies can facilitate faster and cheaper cross-border payments, enabling individuals and businesses in developing countries to send and receive money more easily.
- Microfinance:Blockchain-based platforms can facilitate microloans and other financial services for individuals with limited access to traditional credit.
- Remittances:Cryptocurrencies can reduce the cost and time associated with sending remittances, benefiting migrant workers and their families.
Privacy and Data Security
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology raise concerns about privacy and data security. While blockchain transactions are transparent, the anonymity of users can be a double-edged sword.
- Anonymity and Privacy:The pseudonymous nature of cryptocurrency transactions can provide privacy for individuals, but it also creates challenges for law enforcement and regulatory oversight.
- Data Security:Blockchain technology offers a high level of data security, but it is not immune to attacks, and the potential for data breaches remains a concern.
Ethical Considerations
The development and use of blockchain technology raise ethical considerations, including:
- Transparency and Accountability:The transparency of blockchain transactions can promote accountability, but it can also raise concerns about the potential for misuse of data.
- Environmental Impact:The energy consumption associated with mining some cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, has raised concerns about the environmental impact of the technology.
- Social Equity:The potential for cryptocurrency to exacerbate existing inequalities, with those who have access to technology and resources benefiting more than those who do not.
Future Trends and Predictions: Cryptocurrency And Blockchain: Regulation, Innovation, And Investment
The landscape of cryptocurrency and blockchain is constantly evolving, with new technologies, regulatory changes, and market forces shaping its future. Analyzing emerging trends and making predictions about the future of this sector is essential for understanding its potential impact on society and the global economy.
Emerging Trends
Several key trends are shaping the future of cryptocurrency and blockchain, including:
- Increased Institutional Adoption:Major financial institutions and corporations are increasingly embracing blockchain technology and investing in cryptocurrency assets.
- Regulation and Compliance:Governments and regulatory bodies are developing frameworks to oversee the cryptocurrency and blockchain industry, promoting greater stability and trust.
- Interoperability and Scalability:Efforts are underway to improve the interoperability and scalability of blockchain networks, enabling seamless communication and transactions across different platforms.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi):The emergence of decentralized finance applications, offering alternative financial services without intermediaries.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs):The growing popularity of NFTs, unique digital assets that represent ownership of digital or physical items.
Potential Future Developments
The future of cryptocurrency and blockchain holds significant potential for innovation and disruption. Some potential developments include:
- Mass Adoption of Cryptocurrencies:Cryptocurrencies could become more widely accepted as a form of payment, with increased adoption by businesses and consumers.
- Integration with Existing Systems:Blockchain technology could be integrated with existing financial and other systems, streamlining processes and enhancing efficiency.
- New Applications and Use Cases:The development of new applications and use cases for blockchain technology could lead to significant innovation across various industries.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs):DAOs, organizations governed by smart contracts, could become increasingly popular, disrupting traditional organizational structures.
- Metaverse and Web3:Blockchain technology could play a key role in the development of the metaverse and Web3, decentralized online platforms that offer greater user control and privacy.
Key Trends and Implications
| Trend | Implications |
|---|---|
| Increased Institutional Adoption | Greater market stability and legitimacy, increased liquidity, and broader acceptance of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. |
| Regulation and Compliance | Enhanced consumer protection, reduced risk of fraud and manipulation, and greater confidence in the industry. |
| Interoperability and Scalability | Improved user experience, faster transaction speeds, and greater adoption of blockchain technology across different sectors. |
| Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Disruption of traditional financial services, increased access to financial products and services, and greater control over financial assets. |
| Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) | New opportunities for digital ownership, monetization of digital assets, and innovation in creative industries. |
Wrap-Up
The future of cryptocurrency and blockchain remains dynamic and uncertain, but one thing is clear: this technology has the potential to revolutionize our world. As we navigate the complexities of regulation, innovation, and investment, it is essential to approach this evolving landscape with a balance of enthusiasm and caution.
Understanding the potential benefits and challenges of this transformative technology is crucial for shaping a future where blockchain empowers individuals and communities.
FAQ Compilation
What are the main differences between Bitcoin and Ethereum?
Bitcoin is primarily a digital currency designed for transactions, while Ethereum is a platform that supports smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) in addition to cryptocurrency transactions.
How secure are cryptocurrency transactions?
Cryptocurrency transactions are generally secure due to the use of cryptography and the decentralized nature of blockchain technology. However, security risks can arise from vulnerabilities in exchanges, wallets, or user practices.
What are the environmental concerns associated with cryptocurrency?
The summit also offered a deep dive into the global economic outlook, providing valuable insights for investors navigating uncertain times. Experts at the summit discussed the key drivers of the global economy and the potential impact on different sectors. This discussion encompassed the evolving landscape of technology and its transformative power, specifically focusing on AI and Web3.
Some cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, rely on energy-intensive mining processes, raising concerns about their environmental impact. However, advancements in mining technology and the adoption of more sustainable energy sources are addressing these concerns.