Calculating Taxable Annuity Income 2024: A Guide is essential for understanding how your annuity payments will be taxed. Annuities are complex financial products that offer guaranteed income streams, but the tax implications can be tricky to navigate. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the tax rules surrounding annuities, helping you understand how your annuity income will be taxed and how to plan for potential tax liabilities.
T-C Annuity is a specific type of annuity that offers certain advantages. T-C Annuity 2024 provides details about this annuity and its potential benefits for your retirement planning.
We’ll explore the different types of annuities, the distinction between taxable and non-taxable income, and the role of the “cost basis” in determining taxable income. We’ll also discuss the tax treatment of annuity payments received as a beneficiary and the impact of tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s on annuity income.
Understanding the concept of future value is essential when dealing with annuities. Annuity Is Future Value 2024 explains how annuities can be used to grow your wealth over time.
Understanding Annuity Basics
Annuity contracts are financial instruments that provide a stream of regular payments over a specified period. They are often used for retirement planning, as they offer a guaranteed income stream. Understanding the different types of annuities and their tax implications is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
Annuity Gator is a popular provider of annuity products. Annuity Gator 2024 offers insights into their offerings and how they can help you secure your financial future.
Types of Annuities
- Fixed Annuities:These annuities guarantee a fixed interest rate on your principal investment, providing predictable payments. The payments are usually made for life, but can also be structured for a specific period.
- Variable Annuities:These annuities invest your principal in a portfolio of mutual funds, offering the potential for higher returns but also exposing you to market risk. The payment amounts fluctuate based on the performance of the underlying investments.
- Indexed Annuities:These annuities link your principal to the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. They offer a minimum guaranteed interest rate and potential growth tied to the index’s performance.
Tax Implications of Annuity Payments
Annuity payments are generally taxed as ordinary income, but the tax treatment can vary depending on the type of annuity and the specific contract terms. The portion of each payment that represents a return of your principal investment is not taxed, while the remaining portion is considered taxable income.
Annuity options can vary widely, and understanding the different types is essential. Annuity 3 2024 explores the characteristics of a specific type of annuity, providing insights into its potential benefits and drawbacks.
Examples of Common Annuity Contracts
- Immediate Annuity:Payments begin immediately after the purchase of the annuity. The tax treatment is straightforward, with the payments generally taxed as ordinary income.
- Deferred Annuity:Payments are delayed until a later date, typically during retirement. The tax treatment is more complex, as the payments may be subject to both ordinary income tax and a 10% penalty if withdrawn before age 59 1/2.
Identifying Taxable Annuity Income
Determining the taxable portion of your annuity payments requires understanding the concept of “cost basis.” This represents the amount of your original investment that you are entitled to recover tax-free. The remaining portion of each payment is considered taxable income.
Annuity is primarily used to provide a steady stream of income during retirement. An Annuity Is Primarily Used To Provide 2024 discusses the key purpose of annuities and their role in ensuring financial security in your later years.
Taxable vs. Non-Taxable Income
- Taxable Income:This portion of your annuity payments represents the earnings on your investment. It is subject to federal income tax and may also be subject to state income tax.
- Non-Taxable Income:This portion represents the return of your original investment, also known as the cost basis. It is not subject to taxation.
Cost Basis and Taxable Income
The cost basis is typically calculated as the total amount of premiums paid into the annuity. However, the specific calculation may vary depending on the type of annuity and the contract terms.
Annuity Stream is another provider in the annuity market. Is Annuity Stream 2024 delves into their offerings and helps you determine if they’re the right fit for your needs.
Determining Taxable Income, Calculating Taxable Annuity Income 2024
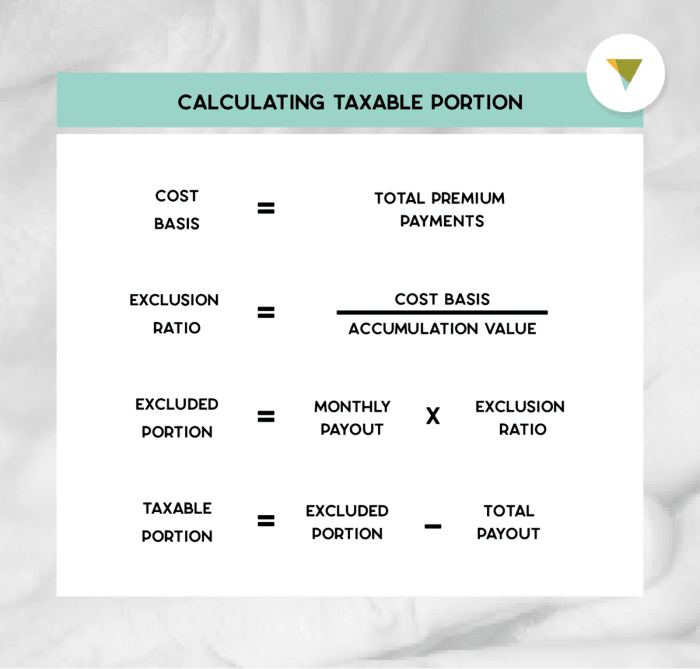
- Calculate your cost basis:This is the total amount of premiums paid into the annuity.
- Determine the annuity payment amount:This is the amount you receive from the annuity each payment period.
- Subtract your cost basis from the total payments received:This difference represents the taxable portion of your annuity income.
Tax Treatment of Annuity Payments: Calculating Taxable Annuity Income 2024
The tax treatment of annuity payments can vary depending on the type of annuity contract and the specific circumstances.
Tax Rules for Different Annuity Contracts
- Fixed Annuities:Payments are typically taxed as ordinary income, with the portion representing the return of your principal investment being tax-free.
- Variable Annuities:Payments are taxed as ordinary income, but the portion representing capital gains is taxed at a lower rate.
- Indexed Annuities:Payments are generally taxed as ordinary income, with the portion representing the return of your principal investment being tax-free.
Early Withdrawals
Withdrawing funds from an annuity before reaching the annuitization period may result in a 10% penalty, in addition to ordinary income tax. This penalty applies to withdrawals made before age 59 1/2, unless certain exceptions apply.
Beneficiary Payments
If you receive annuity payments as a beneficiary, the tax treatment depends on the type of annuity and the specific contract terms. In some cases, the beneficiary may be required to include the payments in their taxable income, while in other cases, the payments may be tax-free.
If you’re considering an annuity in 2024, it’s crucial to understand the potential downsides. Annuity Is Bad 2024 discusses some of the drawbacks you should be aware of, such as limited flexibility and potential for lower returns compared to other investments.
Tax Planning Strategies for Annuities
Several strategies can help minimize your tax liability related to annuity payments.
Understanding how your retirement annuity payments will be calculated is vital. Calculating Retirement Annuity Payments 2024 explains the factors that influence your payment amount and helps you estimate your future income.
Potential Tax Savings Strategies
- Choose the Right Annuity:Selecting an annuity with tax-advantaged features, such as a Roth IRA annuity, can help reduce your tax burden.
- Time Your Withdrawals:Strategically timing your withdrawals to coincide with lower tax brackets can minimize your tax liability.
- Consider Annuitization:Annuities can be structured to provide a guaranteed income stream for life, which can be helpful in managing your tax liability in retirement.
Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Annuities held within tax-advantaged accounts, such as IRAs and 401(k)s, may offer tax benefits during the accumulation phase, but the payments will be taxed as ordinary income during retirement.
An annuity is also known as a “guaranteed income stream” or “retirement income stream.” Annuity Is Also Known As 2024 explores the different terms used to describe this financial product.
Minimizing Tax Liability
Consulting with a qualified tax professional can help you develop a comprehensive tax planning strategy that addresses your individual circumstances and maximizes your tax savings potential.
2024 Tax Changes Affecting Annuities
While there are no significant tax law changes specifically targeting annuities in 2024, it’s crucial to stay informed about any potential changes that could affect your tax planning.
Annuity is a financial product that can play a significant role in your retirement planning. Annuity Is What 2024 provides a comprehensive overview of what an annuity is and how it works.
Potential Changes
- Changes to the Tax Treatment of Annuity Withdrawals:It’s always possible that tax legislation could change the tax treatment of annuity withdrawals, impacting the amount of taxable income.
Impact on Tax Planning
Staying informed about any potential tax law changes is crucial for adjusting your tax planning strategies and ensuring you maximize your tax savings. Consulting with a qualified tax professional can help you navigate these changes and develop a comprehensive tax plan.
Illustrative Examples
The following table showcases various annuity scenarios and their corresponding taxable income calculations:
| Annuity Type | Cost Basis | Payment Amount | Taxable Income |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Annuity | $100,000 | $6,000 | $1,000 |
| Variable Annuity | $150,000 | $8,000 | $2,000 |
| Indexed Annuity | $200,000 | $10,000 | $3,000 |
Example 1:A fixed annuity with a cost basis of $100,000 pays $6,000 per year. The taxable income is calculated as follows:* Taxable Income = Payment Amount
Calculating your annual annuity payments is crucial for financial planning. How To Calculate Annual Annuity 2024 provides a guide to help you determine the amount you can expect to receive each year.
- Cost Basis / Number of Payments
- Taxable Income = $6,000
- $100,000 / 20 = $1,000
Example 2:A variable annuity with a cost basis of $150,000 pays $8,000 per year. The taxable income is calculated as follows:* Taxable Income = Payment Amount
When considering an annuity, the exclusion ratio is a key factor to understand. Annuity Exclusion Ratio 2024 explains how this ratio impacts your taxes and can help you make informed decisions about your retirement planning.
- Cost Basis / Number of Payments
- Taxable Income = $8,000
- $150,000 / 25 = $2,000
Example 3:An indexed annuity with a cost basis of $200,000 pays $10,000 per year. The taxable income is calculated as follows:* Taxable Income = Payment Amount
Before you choose an annuity provider, it’s essential to research their legitimacy. Is Annuity Gator Legit 2024 explores the reputation and trustworthiness of this particular provider.
- Cost Basis / Number of Payments
- Taxable Income = $10,000
- $200,000 / 30 = $3,000
End of Discussion
Understanding the tax implications of annuities is crucial for maximizing your retirement income. By carefully considering your annuity choices and utilizing available tax planning strategies, you can ensure that you receive the most beneficial tax treatment for your annuity payments.
Calculating the right retirement annuity can be complex. Calculating Retirement Annuity 2024 provides guidance on factors to consider and methods to ensure you’re setting yourself up for a comfortable retirement.
This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the key aspects of calculating taxable annuity income, empowering you to make informed decisions and minimize your tax liability. Remember, consulting with a qualified financial advisor is recommended to tailor your tax planning strategy to your specific financial circumstances.
Helpful Answers
What is the difference between a fixed and variable annuity?
A fixed annuity provides a guaranteed rate of return, while a variable annuity’s return is tied to the performance of underlying investments. The tax implications can differ between the two.
The 59.5 rule is a crucial aspect of annuities. Annuity 59.5 Rule 2024 explains how this rule impacts your ability to withdraw funds from your annuity without penalties.
How do I calculate my cost basis for an annuity?
Your cost basis is the amount of money you invested in the annuity, including premiums and any contributions. It’s used to determine the taxable portion of your annuity payments.
Are annuity payments subject to Social Security taxes?
Generally, annuity payments are not subject to Social Security taxes. However, there are some exceptions, so it’s important to consult with a tax professional.
What are some tax planning strategies for annuities?
Some strategies include timing withdrawals to minimize your tax liability, considering tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s, and working with a financial advisor to develop a comprehensive tax plan.




