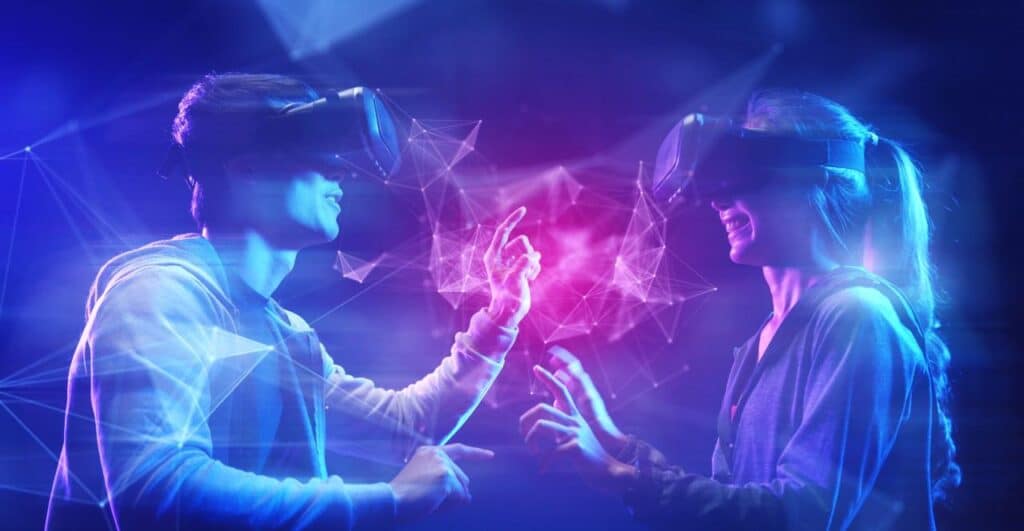
The Metaverse and Web3: Building the Future of the Internet, this exploration delves into a transformative landscape where digital and physical realms converge. This convergence promises to reshape our online interactions, redefine our understanding of ownership, and unlock a new era of digital empowerment.
The metaverse, a nascent concept, envisions a persistent, immersive digital environment where users can interact with each other, participate in virtual experiences, and create and own digital assets. This virtual realm, powered by advancements in virtual reality, augmented reality, and blockchain technology, holds the potential to revolutionize industries like gaming, entertainment, education, and healthcare.
The Metaverse: A New Frontier for the Internet
The internet has undergone a remarkable evolution, transforming from a simple network of interconnected computers to a dynamic platform that shapes our lives in profound ways. This journey has been marked by significant technological advancements, each ushering in a new era of connectivity and innovation.
From the early days of Web 1.0, where users primarily consumed static content, we have progressed to Web 2.0, characterized by social media, user-generated content, and the rise of mobile devices. Now, we stand on the cusp of Web 3.0, a decentralized and user-centric internet powered by blockchain technology, artificial intelligence, and the metaverse.The metaverse, a term coined by science fiction writer Neal Stephenson in his 1992 novel “Snow Crash,” envisions a persistent, immersive virtual world where users can interact with each other and digital objects in a seamless and realistic manner.
This immersive experience is enabled by technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), which blur the lines between the physical and digital realms.
Evolution of the Internet
- Web 1.0 (1990s):This era was characterized by static websites, limited interactivity, and a focus on information dissemination. Users primarily consumed content, with minimal opportunities for engagement or collaboration. Key technologies included HTML, HTTP, and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
- Web 2.0 (2000s-present):The rise of social media, user-generated content, and cloud computing marked the arrival of Web 2.0. This era witnessed the emergence of platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter, empowering users to create and share content, connect with others, and participate in online communities.
Key technologies included JavaScript, AJAX, and social media APIs.
- Web 3.0 (Present and beyond):The next evolution of the internet, Web 3.0, emphasizes decentralization, user ownership, and interoperability. Blockchain technology, artificial intelligence, and the metaverse are key drivers of this shift. Web 3.0 aims to create a more open, transparent, and secure internet, empowering users to control their data, participate in decentralized governance, and engage in immersive digital experiences.
The Metaverse: A Virtual World of Possibilities, The Metaverse and Web3: Building the Future of the Internet
The metaverse can be understood as a persistent, shared virtual world where users can interact with each other and digital objects in a seamless and realistic manner. This immersive experience is enabled by technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR).
Core Features of the Metaverse
- Immersive Experiences:The metaverse aims to provide users with highly immersive experiences, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. VR, AR, and MR technologies create realistic environments that engage multiple senses, allowing users to feel present in the virtual world.
- Virtual Reality (VR):VR technology creates completely immersive experiences, immersing users in virtual environments using headsets and other devices. Users can interact with virtual objects and environments, creating a sense of presence and agency.
- Augmented Reality (AR):AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their surroundings. AR applications can provide interactive experiences, such as virtual shopping, gaming, and navigation.
- Mixed Reality (MR):MR combines elements of VR and AR, creating a hybrid experience where virtual objects and environments interact with the real world. MR applications can enable users to interact with virtual objects in their physical space, creating a more integrated and dynamic experience.
The Metaverse vs. the Current Internet
The metaverse represents a significant departure from the current internet, offering a fundamentally different user experience and paradigm for content creation and ownership.
Key Differences
- User Interaction:The metaverse emphasizes real-time, immersive interaction, allowing users to engage with each other and the virtual environment in a more dynamic and engaging manner. This contrasts with the current internet, where interaction is primarily limited to text-based communication and static content.
- Content Creation:The metaverse empowers users to create and share content in a more immersive and interactive manner. Users can design virtual worlds, build objects, and create experiences that go beyond the limitations of traditional web platforms.
- Ownership:The metaverse emphasizes user ownership of digital assets, enabling users to acquire, trade, and monetize their virtual creations. This contrasts with the current internet, where ownership is often centralized and controlled by platform providers.
Impact of the Metaverse on Various Sectors
The metaverse has the potential to transform various sectors, bringing new opportunities and challenges across industries.
Potential Applications
- Gaming:The metaverse offers a platform for immersive and interactive gaming experiences, blurring the lines between virtual and real-world play. Users can engage in collaborative gameplay, explore vast virtual worlds, and participate in virtual economies.
- Entertainment:The metaverse can revolutionize entertainment, providing users with immersive concerts, virtual theaters, and interactive experiences. Users can attend virtual events, interact with celebrities, and enjoy personalized entertainment experiences.
- Education:The metaverse offers a platform for engaging and interactive learning experiences, enabling students to explore virtual environments, participate in simulations, and collaborate with peers from around the world.
- Healthcare:The metaverse can facilitate remote healthcare consultations, surgical simulations, and patient education. Virtual reality applications can help patients manage pain, reduce anxiety, and improve rehabilitation outcomes.
Examples of Existing Metaverse Platforms
Several metaverse platforms are emerging, each offering unique functionalities and experiences.
Platform Examples
- Meta’s Horizon Worlds:Meta’s Horizon Worlds is a social VR platform where users can create and explore virtual worlds, interact with others, and engage in social activities. It offers a platform for building communities, socializing, and enjoying immersive experiences.
- Sandbox:Sandbox is a decentralized metaverse platform that allows users to create, own, and trade virtual assets. It empowers users to build games, experiences, and virtual worlds, leveraging blockchain technology for secure ownership and interoperability.
- Decentraland:Decentraland is a decentralized virtual world built on the Ethereum blockchain. Users can own virtual land, create applications, and participate in a decentralized governance system. It offers a platform for building communities, exploring virtual worlds, and engaging in decentralized economies.
A Hypothetical Scenario: The Metaverse in Everyday Life
Imagine a future where the metaverse seamlessly integrates into our daily lives, transforming the way we work, learn, and socialize.
Scenario:
Imagine a world where you can attend virtual meetings in immersive environments, collaborate with colleagues from around the globe, and share ideas in a more engaging and interactive manner. You can also access virtual libraries, attend online courses, and connect with experts in a more personalized and interactive way.
In your free time, you can explore virtual worlds, attend virtual concerts, and socialize with friends in immersive environments. The metaverse can even provide access to personalized healthcare services, enabling you to consult with doctors, manage your health, and engage in virtual rehabilitation programs.
The summit also delved into the evolving landscape of leadership, exploring the importance of purpose, resilience, and the role of the next generation. Leadership Reimagined: Purpose Resilience And The Next Generation emphasized the need for leaders who can navigate complex challenges and inspire others.
These discussions underscored the critical role of technology in shaping the future of leadership and its impact on investment strategies.
Conclusion: The Metaverse And Web3: Building The Future Of The Internet
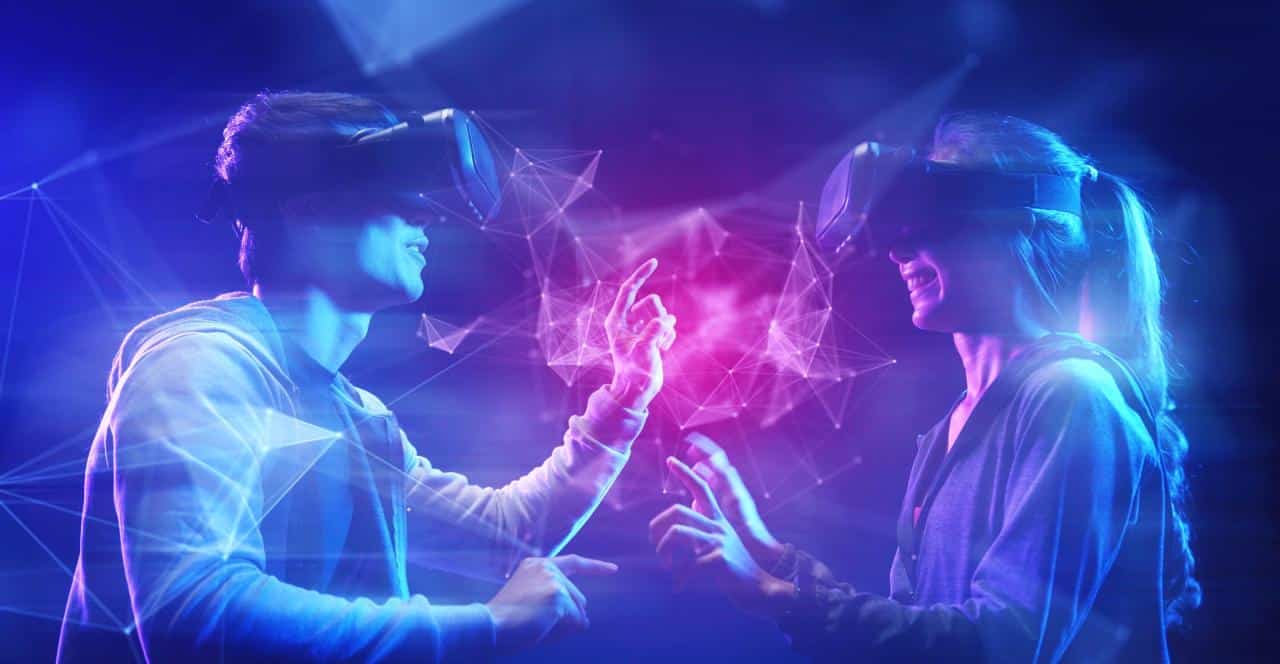

The metaverse and Web3 represent a paradigm shift in how we interact with technology and each other. By merging the immersive potential of the metaverse with the decentralized principles of Web3, we are on the cusp of a digital revolution that will redefine our online experiences, empower individuals, and unlock new possibilities for innovation.
Decoding the global economic outlook is crucial for investors, and the Dealbook Summit 2024 offered valuable perspectives on this complex topic. Dealbook Summit 2024: Decoding The Global Economic Outlook highlighted the transformative power of technology, particularly in areas like AI and Web3.
Technology’S Transformative Power is reshaping industries and creating new opportunities for investors.
As we navigate this exciting new frontier, it is crucial to consider the ethical implications, ensure equitable access, and foster responsible development to harness the full potential of this transformative technology.
General Inquiries
What are some examples of existing metaverse platforms?
The Dealbook Summit 2024, a hub for investors, offered invaluable insights on navigating the ever-changing economic landscape. Key takeaways for investors included understanding the rise of emerging markets, which present both exciting opportunities and unique challenges. The Rise Of Emerging Markets: New Opportunities And Challenges provided a framework for navigating these dynamic environments.
Popular metaverse platforms include Decentraland, Sandbox, and Axie Infinity. Each platform offers unique functionalities, including virtual land ownership, game development, and community building.
How does Web3 differ from Web 2.0?
While Web 2.0 is characterized by centralized platforms and data ownership, Web3 emphasizes decentralization, user ownership, and transparency through blockchain technology.
What are the potential risks associated with the metaverse?
Potential risks include data privacy concerns, cybersecurity threats, and the potential for digital inequality if access to the metaverse is not equitable.
What is the role of NFTs in the metaverse?
NFTs play a crucial role in the metaverse by enabling digital ownership of virtual assets, such as avatars, virtual land, and digital collectibles.