Annuity 1099 2024 sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Understanding the tax implications of your annuity payments in 2024 is crucial for maximizing your retirement income.
Kathy’s annuity might be experiencing some challenges in 2024. It’s important to understand the potential issues that can arise with annuities and how to address them. For more information on Kathy’s specific situation, check out this article: Kathy’s Annuity Is Currently Experiencing 2024.
This guide will explore the different types of annuities, the tax rules governing payments, and strategies for minimizing your tax burden. Whether you’re receiving traditional or Roth annuity payments, this comprehensive overview will provide valuable insights into how to navigate the complexities of annuity taxation.
Are annuity payments exempt from taxes? The tax treatment of annuities can vary depending on factors such as the type of annuity and your individual circumstances. For more information on the taxability of annuities, check out this article: Is Annuity Exempt From Tax 2024.
From deciphering the intricacies of Form 1099-R to understanding the impact of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, this guide will equip you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about your retirement income. We’ll delve into the factors that determine whether your annuity payments are taxable or non-taxable, explain the concept of the “exclusion ratio,” and demonstrate how to report annuity income on your federal tax return.
A joint life annuity is an option that provides payments for the lifetime of two individuals, typically a couple. It can be a helpful option for those who want to ensure that their surviving spouse will continue to receive payments after their death.
To learn more about joint life annuities, check out this article: Annuity Joint Life Option 2024.
We’ll also explore common annuity tax planning strategies to help you optimize your tax efficiency and maximize your retirement savings.
Understanding Annuities and Form 1099
Annuities are financial products that provide a stream of payments over time, often used for retirement planning. These payments can be subject to taxation, and the specific rules governing their tax treatment can be complex. Understanding the different types of annuities, their tax implications, and how they are reported on Form 1099-R is crucial for anyone receiving annuity payments.
Types of Annuities and Their Tax Implications
Annuities can be broadly categorized into two main types: traditional annuities and Roth annuities. Each type has distinct tax characteristics.
- Traditional Annuities:Contributions to traditional annuities are typically tax-deductible, but the payments received in retirement are taxable as ordinary income. This means you’ll pay taxes on the entire amount of the annuity payment.
- Roth Annuities:Contributions to Roth annuities are not tax-deductible, but the payments received in retirement are tax-free. This means you won’t pay any taxes on the annuity payments, but you will have paid taxes on the contributions upfront.
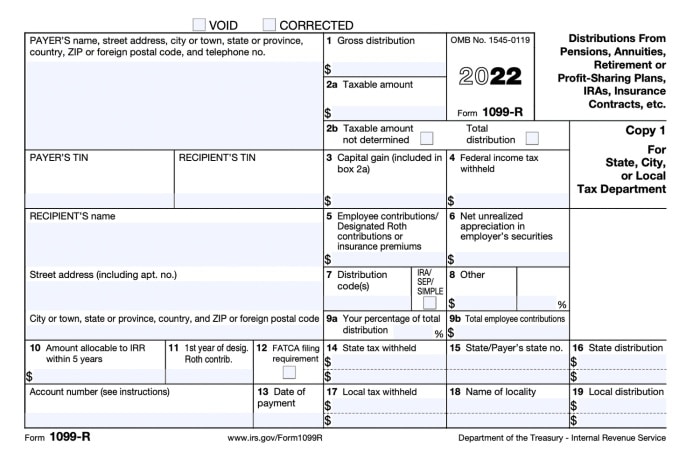
Form 1099-R: Reporting Annuity Payments
Form 1099-R, “Taxable Distributions from Pensions, Annuities, Retirement or Profit-Sharing Plans, IRAs, Insurance Contracts, etc.,” is used to report distributions from annuities and other retirement plans. This form provides crucial information for tax purposes, including:
- Amount of the distribution:The total amount of the annuity payment received during the tax year.
- Taxable portion of the distribution:This portion represents the amount of the payment that is subject to taxation. It may include both earnings and a portion of the original contributions.
- Non-taxable portion of the distribution:This portion represents the amount of the payment that is not subject to taxation, typically consisting of the original contributions.
- Code for the distribution:This code indicates the type of distribution, such as a regular payment, withdrawal, or rollover.
Comparing Tax Treatment of Traditional and Roth Annuities
The tax treatment of traditional and Roth annuities differs significantly. The following table highlights the key distinctions:
| Feature | Traditional Annuity | Roth Annuity |
|---|---|---|
| Contributions | Tax-deductible | Not tax-deductible |
| Payments in Retirement | Taxable as ordinary income | Tax-free |
Annuity Payments in 2024
The tax rules for annuity payments received in 2024 remain largely unchanged from previous years. However, certain aspects of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) have impacted the taxation of annuities.
Tax Rules for Annuity Payments in 2024
- Traditional Annuities:Payments from traditional annuities are taxed as ordinary income. The taxable portion of the payment is calculated using the “exclusion ratio,” which represents the proportion of the payment that represents a return of your original contributions.
- Roth Annuities:Payments from Roth annuities are tax-free. This means you won’t pay any federal income tax on the payments, but you will have paid taxes on the contributions upfront.
Impact of the TCJA on Annuity Taxation
The TCJA introduced several changes to the tax code, including:
- Increased Standard Deduction:The standard deduction for individuals and married couples was increased, potentially reducing the taxable income from annuity payments.
- Lower Tax Rates:The TCJA lowered individual income tax rates, which could reduce the tax burden on annuity payments for some taxpayers.
Reporting Annuity Payments on Federal Income Tax Returns
Annuity payments are reported on Schedule B of Form 1040. The specific details of how annuity payments are reported depend on the type of annuity and the tax treatment of the payments.
Are you wondering if the taxes on your annuity are deferred? The tax treatment of annuities can be complicated, and understanding how they are taxed is crucial for financial planning. Check out this article to learn more about tax deferral with annuities: Is Annuity Tax Deferred 2024.
- Traditional Annuities:The taxable portion of the annuity payment is reported on line 4a of Schedule B. The non-taxable portion of the payment is reported on line 4b.
- Roth Annuities:Payments from Roth annuities are not reported on Schedule B, as they are tax-free.
Taxable and Non-Taxable Annuity Payments: Annuity 1099 2024
The taxability of an annuity payment depends on several factors, including the type of annuity, the payment structure, and the amount of the original contributions. The concept of the “exclusion ratio” plays a key role in determining the taxable portion of an annuity payment.
Factors Determining Taxability of Annuity Payments
- Type of Annuity:Traditional annuities generally result in taxable payments, while Roth annuities typically have tax-free payments.
- Payment Structure:Annuity payments can be structured as a fixed amount or a variable amount, with different tax implications.
- Original Contributions:The amount of the original contributions to the annuity influences the taxable portion of the payment.
The Exclusion Ratio, Annuity 1099 2024
The exclusion ratio is a fraction that determines the portion of each annuity payment that represents a return of your original contributions. This portion is considered non-taxable. The exclusion ratio is calculated as follows:
Exclusion Ratio = Original Contributions / Expected Total Payments
For example, if you contributed $100,000 to a traditional annuity and expect to receive $200,000 in total payments, the exclusion ratio would be 0.5 (100,000 / 200,000). This means that 50% of each annuity payment would be non-taxable, and 50% would be taxable.
Taxability of Different Annuity Payments
The following table summarizes the taxability of different types of annuity payments:
| Type of Annuity | Taxability |
|---|---|
| Traditional Annuity Payments | Taxable as ordinary income, subject to the exclusion ratio |
| Roth Annuity Payments | Tax-free |
| Annuity Payments from a Qualified Retirement Plan | Taxable as ordinary income |
| Annuity Payments from a Non-Qualified Retirement Plan | Taxable as ordinary income |
Reporting Annuity Payments on Form 1040
Annuity income is reported on Schedule B of Form 1040. The specific steps involved in reporting annuity income depend on the type of annuity and the tax treatment of the payments. The following guide provides a step-by-step process for reporting annuity income on Schedule B.
The basis of an annuity is an important factor to consider, especially for tax purposes. It represents the amount of your original investment that is not subject to taxes. For more information on the basis of annuities, check out this article: Annuity Basis Is 2024.
Step-by-Step Guide for Reporting Annuity Income
- Gather Your Form 1099-R:Obtain your Form 1099-R from the annuity provider. This form will contain details about your annuity payments for the tax year.
- Determine the Taxable Portion of the Payments:Calculate the taxable portion of your annuity payments using the exclusion ratio. If you received payments from a Roth annuity, the entire amount is tax-free.
- Report on Schedule B:Enter the taxable portion of your annuity payments on line 4a of Schedule B. If you received payments from a Roth annuity, you do not need to report them on Schedule B.
- Complete the Rest of Form 1040:Continue completing the rest of Form 1040, including other sources of income and deductions.
Sample Form 1040 with Hypothetical Annuity Payments
Here is a sample Form 1040 with hypothetical annuity payments and their corresponding tax treatment. Please note that this is for illustrative purposes only and should not be used as tax advice.
Scenario:John received $10,000 in annuity payments from a traditional annuity during the tax year. His original contributions to the annuity were $50,000, and he expects to receive a total of $100,000 in payments. He also received $5,000 in tax-free payments from a Roth annuity.
Form 1040:
Annuity drawdown is a popular option for retirees, allowing them to take out money from their annuity as needed. However, it’s important to understand how drawdown works and what the potential implications are. To learn more about annuity drawdown, check out this article: Is Annuity Drawdown 2024.
Schedule B: Interest and Ordinary Dividends
Line 4a: Taxable portion of annuity payments (50% of $10,000) = $5,000
Have questions about annuities? You’re not alone! Many people have questions about how annuities work, their tax implications, and other aspects. Check out this article for answers to common annuity questions: Annuity Questions And Answers 2024.
Line 4b: Non-taxable portion of annuity payments (50% of $10,000) = $5,000
Many people are curious about the duration of annuity payments. While some annuities have a fixed term, others can last indefinitely. If you’re interested in learning more about annuities with indefinite durations, check out this article: Annuity Is Indefinite Duration 2024.
Tax Treatment:The $5,000 taxable portion of the annuity payment is reported on line 4a of Schedule B. The $5,000 non-taxable portion is reported on line 4b. The $5,000 tax-free payment from the Roth annuity is not reported on Schedule B.
Calculating the Taxable Portion of an Annuity Payment
To calculate the taxable portion of an annuity payment, use the following formula:
Taxable Portion = Annuity Payment
If you’re in the UK, you might be interested in learning more about annuities available there. The UK annuity market has its own unique features and regulations. Check out this article for more information on annuities in the UK: Annuity Uk 2024.
(Exclusion Ratio x Annuity Payment)
For example, if John’s annuity payment was $1,000 and his exclusion ratio was 0.5, the taxable portion of the payment would be:
Taxable Portion = $1,000
Can you still work while receiving an annuity? The answer is yes, you can. Annuity payments are not typically affected by your employment status. For more information on receiving an annuity while working, check out this article: Can You Receive Annuity And Still Work 2024.
(0.5 x $1,000) = $500
If your annuity is out of surrender, it means that you can no longer withdraw your principal investment without penalty. Understanding the surrender period and its implications is important for managing your annuity. Check out this article for more information: My Annuity Is Out Of Surrender 2024.
Common Annuity Tax Planning Strategies
There are several strategies that can be employed to minimize the tax burden on annuity payments. These strategies involve structuring annuity payments to maximize tax efficiency.
Strategies for Minimizing Tax Burden
- Timing of Withdrawals:Timing withdrawals from an annuity can impact the tax consequences. For example, withdrawing a larger portion of the annuity in a year with a lower tax bracket could reduce your overall tax liability.
- Spreading Out Payments:Spreading out annuity payments over several years can help reduce the taxable income in any given year. This can be particularly beneficial for those in higher tax brackets.
- Using the Exclusion Ratio:Understanding and applying the exclusion ratio correctly can help you identify the non-taxable portion of your annuity payments and minimize your tax liability.
Structuring Annuity Payments for Tax Optimization
The way you structure annuity payments can have a significant impact on your tax liability. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Fixed vs. Variable Payments:Fixed annuity payments provide a predictable stream of income, while variable payments are subject to market fluctuations. The tax implications of each type can differ, so consider your risk tolerance and tax situation.
- Lump-Sum Payments:Receiving a lump-sum payment from an annuity can be advantageous if you can invest the funds and generate tax-efficient returns. However, you’ll need to consider the potential tax consequences of a large lump-sum payment.
Potential Tax Implications of Early Withdrawals
Withdrawing from an annuity before reaching the designated start date can trigger penalties and taxes. The specific rules vary depending on the type of annuity and the terms of the contract. It’s crucial to consult with a tax professional before making any early withdrawals.
Final Review
By understanding the tax rules surrounding annuities and implementing effective planning strategies, you can navigate the complexities of retirement income with confidence. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the key considerations for annuity taxation in 2024. Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions to maximize your retirement income and ensure a comfortable and financially secure future.
Trying to figure out how much you can withdraw from your annuity each year? A withdrawal calculator can be a helpful tool. There are various calculators available online, and they can be a great resource for planning your retirement income.
Check out this article for more information on annuity withdrawal calculators: Annuity Withdrawal Calculator 2024.
Clarifying Questions
What is the difference between a traditional and a Roth annuity?
Are annuities the same as IRAs? While both are retirement savings options, there are important differences between them. If you’re considering an annuity, it’s crucial to understand how it differs from an IRA. This article provides more information: Is Annuity The Same As Ira 2024.
A traditional annuity allows for tax-deferred growth, meaning you won’t pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw them in retirement. Roth annuities, on the other hand, involve contributions with after-tax dollars, but your withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
How do I determine the taxable portion of my annuity payments?
The taxable portion of your annuity payments is calculated using the “exclusion ratio,” which is determined by dividing the amount of your original investment in the annuity by the total expected payments from the annuity. This ratio is then multiplied by each annuity payment to determine the non-taxable portion, with the remaining amount considered taxable income.
If you’re concerned about the religious implications of annuities, you might be wondering if they are considered halal. The question of whether or not annuities are halal is a complex one, and the answer may depend on specific factors.
For a deeper dive into this topic, check out this article: Is Annuity Halal 2024.
Can I withdraw from my annuity early without penalty?
Generally, early withdrawals from an annuity before age 59 1/2 are subject to a 10% penalty, in addition to regular income taxes. However, there are some exceptions to this rule, such as for qualified medical expenses or certain disability situations.
Are all annuity payments taxable?
No, not all annuity payments are taxable. The taxability of your annuity payments depends on the type of annuity, the source of the funds, and the age at which you start receiving payments. For example, Roth annuity withdrawals are generally tax-free, while traditional annuity withdrawals are taxable.
What are some common annuity tax planning strategies?
Some common annuity tax planning strategies include: (1) choosing the right type of annuity based on your tax situation, (2) timing your annuity withdrawals to minimize taxes, (3) considering a Roth conversion, and (4) consulting with a tax advisor to develop a personalized plan.
Wondering if your annuity income is subject to taxes in India? You’re not alone. Many people have questions about the tax implications of annuities, especially in 2024. Find out more about how annuities are taxed in India by checking out this article: Is Annuity Taxable In India 2024.






