The Roth IRA contribution limit for self-employed individuals in 2024 presents a unique opportunity to save for retirement while potentially minimizing future tax burdens. As a self-employed individual, you have the flexibility to contribute to a Roth IRA, which allows for tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
This article explores the ins and outs of Roth IRA contributions for self-employed individuals, including the contribution limit, eligibility criteria, tax implications, and effective contribution strategies.
Understanding the nuances of Roth IRA contributions for self-employed individuals is crucial for maximizing retirement savings and achieving financial security. This article will delve into the specifics of contribution limits, eligibility requirements, and the tax benefits associated with this popular retirement savings vehicle.
Roth IRA Contribution Limit Basics: Roth IRA Contribution Limit For Self-employed Individuals In 2024
The Roth IRA contribution limit for self-employed individuals in 2024 is the same as for everyone else: $7,000. This means that you can contribute up to $7,000 to your Roth IRA for the year. If you’re 50 or older, you can contribute an additional $1,000as a “catch-up” contribution, bringing your total limit to $8,000.
The maximum 401k contribution for 2024 is $22,500 for individuals under age 50 and $30,000 for those 50 and older. This limit can help you determine how much you can contribute to your retirement savings.
The Difference Between Traditional IRA and Roth IRA Contribution Limits
The contribution limit for a traditional IRA is the same as for a Roth IRA. However, there are some key differences between the two types of IRAs when it comes to contributions.The main difference between traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs lies in when you pay taxes.
With a traditional IRA, you don’t pay taxes on your contributions until you withdraw the money in retirement. With a Roth IRA, you pay taxes on your contributions now, but you don’t have to pay taxes on withdrawals in retirement.
Sole proprietorships have a tax extension deadline of October 15, 2024. This deadline gives you extra time to file your taxes, but it’s important to remember that you still need to pay any taxes owed by the original deadline.
Calculating the Contribution Limit for Self-Employed Individuals
If you’re self-employed, you’ll need to make your Roth IRA contributions through a self-directed IRA, also known as a Solo 401(k). This is because you’re both the employer and the employee in your own business.You can contribute to both the employee and employer portions of your Solo 401(k).
For 2024, the total contribution limit for both portions is $66,000. This includes the $7,000 (or $8,000 if you’re 50 or older) limit for the employee portion and the $60,000limit for the employer portion.The employer portion of your Solo 401(k) contribution is calculated as a percentage of your net adjusted self-employment income.
The tax brackets for 2024 have been adjusted to reflect inflation. Understanding these changes is important for planning your taxes and potentially adjusting your income or deductions.
This income is calculated by subtracting your business expenses from your gross income.For example, let’s say your net adjusted self-employment income for the year is $100,000. You can contribute up to $60,000as an employer contribution to your Solo 401(k).
Single filers have a specific contribution limit for Roth IRAs in 2024. Knowing the contribution limit can help you plan your retirement savings and maximize your tax benefits.
This is calculated by multiplying your net adjusted self-employment income by 60% (the maximum contribution limit for the employer portion).
The employer portion of your Solo 401(k) contribution is calculated as a percentage of your net adjusted self-employment income.
You can choose to contribute more to the employee portion of your Solo 401(k) if you wish, up to the maximum contribution limit of $7,000(or $8,000 if you’re 50 or older).
If you have a SIMPLE IRA, the contribution limits for 2024 are important to know. This information can help you maximize your retirement savings within the allowed limits.
Eligibility Criteria
While anyone can open a Roth IRA, there are specific eligibility criteria for contributing to a Roth IRA as a self-employed individual. These requirements are different from those for traditional employees, and they primarily revolve around income limitations.
The contribution limits for traditional 401k plans in 2024 are $22,500 for individuals under age 50 and $30,000 for those 50 and older. Understanding these limits is important for planning your retirement savings.
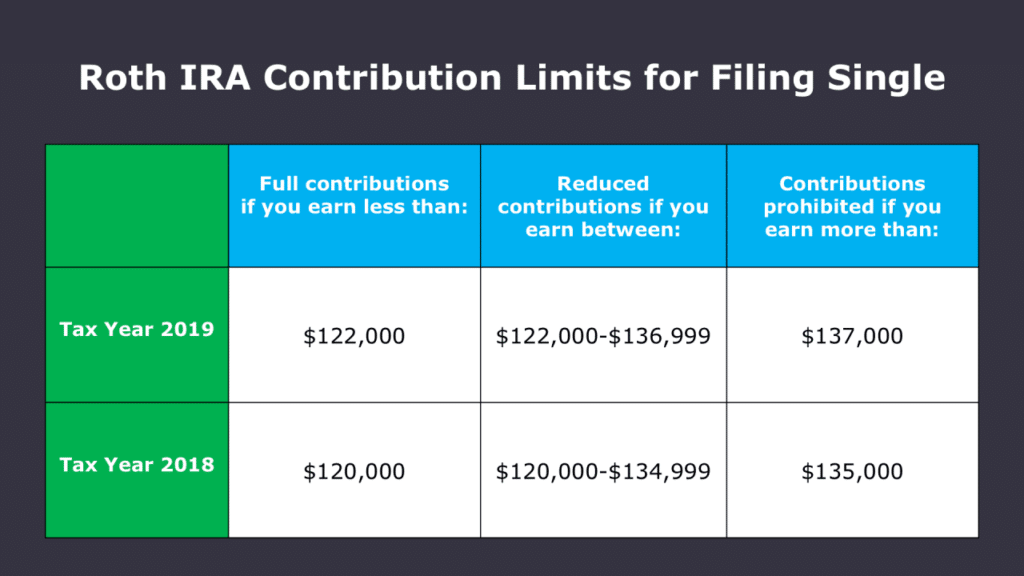
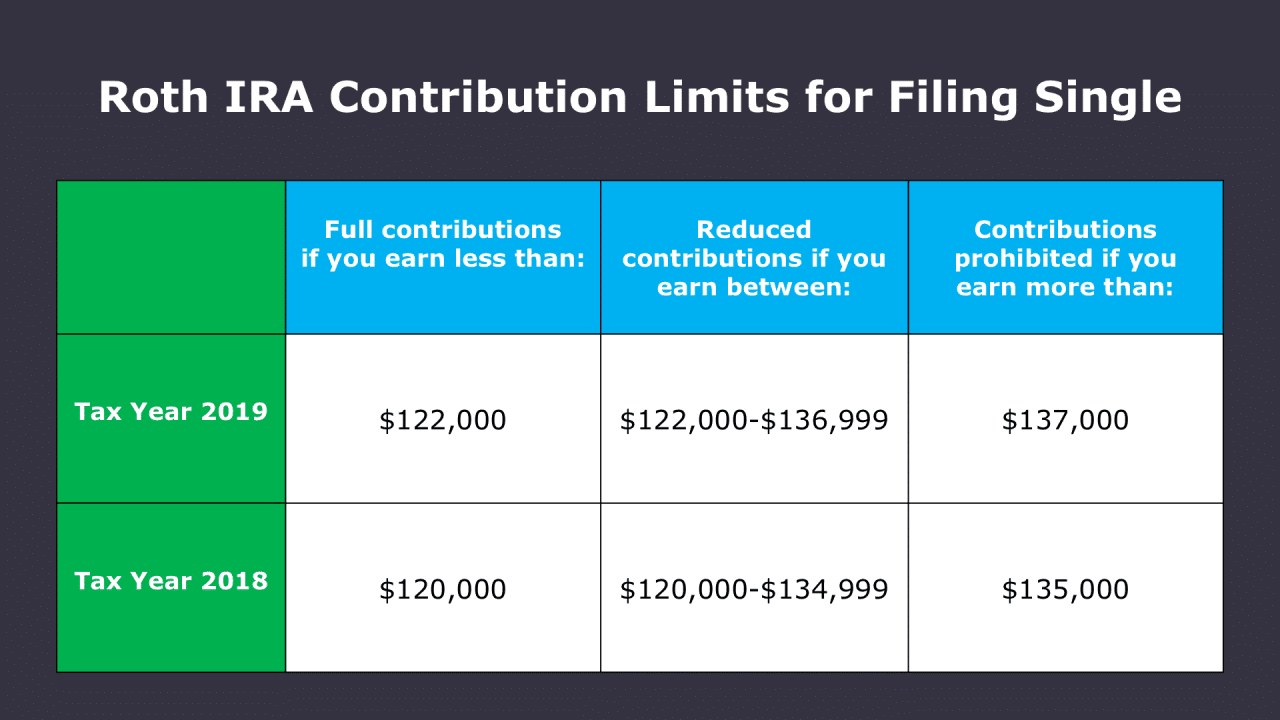
Income Limitations
The ability to contribute to a Roth IRA for self-employed individuals is determined by your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI). MAGI is your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) plus certain deductions that are not included in AGI.
Saving for retirement is important, and knowing the maximum 401k contribution for 2024 can help you maximize your retirement savings. The contribution limit for 2024 is $22,500 for individuals under age 50 and $30,000 for those 50 and older.
The 2024 Roth IRA contribution limit for self-employed individuals is $15,500 for individuals and $31,000 for married couples filing jointly.
Businesses need to understand the W9 Form requirements for October 2024. The W9 Form is used to provide your taxpayer identification number (TIN) to businesses or organizations that need to report payments made to you.
This means that if your MAGI exceeds these thresholds, you may not be able to contribute the full amount to your Roth IRA.
The 401k contribution limit may change in 2024. It’s important to stay updated on these changes to ensure you are maximizing your retirement savings.
Deductibility and Tax Implications
Unlike traditional IRAs, Roth IRA contributions are not tax-deductible. This means you won’t be able to claim a deduction for your Roth IRA contributions on your tax return. However, the trade-off is that your Roth IRA contributions grow tax-free and withdrawals in retirement are also tax-free.
Independent contractors need to understand the W9 Form requirements for October 2024. This form is essential for businesses or organizations to report payments made to you.
Tax Implications of Roth IRA Contributions
The tax implications of Roth IRA contributions for self-employed individuals are as follows:* Tax-Free Growth:Your Roth IRA contributions grow tax-free, meaning you won’t have to pay taxes on any earnings or investment gains within the account. This can lead to significant tax savings over time, especially in retirement.
Tax-Free Withdrawals
When you withdraw money from your Roth IRA in retirement, you won’t have to pay any taxes on the withdrawals. This is a major advantage over traditional IRAs, where withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income.
The tax brackets for 2024 in the United States are based on your taxable income. Understanding these brackets can help you plan your taxes and potentially adjust your income or deductions.
No Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs)
People with disabilities may be eligible for a higher standard deduction in 2024. This deduction can help reduce your taxable income and potentially lower your tax liability.
Unlike traditional IRAs, there are no required minimum distributions (RMDs) for Roth IRAs. This means you can let your money grow tax-free for as long as you want without having to take any withdrawals.
Retirement planning is crucial, and a tax calculator can be a valuable tool for retirees in October 2024. It can help you understand your tax liability and plan accordingly for your retirement income.
Comparison with Traditional IRA
The tax treatment of Roth IRA contributions differs significantly from traditional IRA contributions for self-employed individuals. Here’s a breakdown:
| Feature | Roth IRA | Traditional IRA |
|---|---|---|
| Contribution Deductibility | Not Deductible | Deductible |
| Tax Treatment of Growth | Tax-Free | Tax-Deferred |
| Tax Treatment of Withdrawals | Tax-Free | Taxed as Ordinary Income |
| Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) | None | Yes, after age 73 |
Example:Let’s say you contribute $6,500 to a Roth IRA in 2024 and the account grows to $100,000 by the time you retire. When you withdraw the $100,000, you won’t have to pay any taxes on it. This is because you already paid taxes on the $6,500 contribution when you earned it.
You may be able to get an extension on your taxes if you owe money in October 2024. However, it’s important to note that an extension only gives you more time to file, not to pay. You’ll still need to pay any taxes owed by the original deadline.
Contribution Strategies for Self-Employed Individuals
Maximizing your Roth IRA contributions as a self-employed individual requires strategic planning. By understanding the available options and their implications, you can optimize your retirement savings.
Contribution Strategies for Self-Employed Individuals
Self-employed individuals have unique opportunities to maximize their Roth IRA contributions. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Maximize Contributions:The annual contribution limit for Roth IRAs in 2024 is $7,500. Self-employed individuals can contribute this full amount, even if they have other retirement accounts, such as a Solo 401(k).
- Contribute Early:The power of compounding works best when you start saving early. The earlier you begin contributing, the more time your money has to grow.
- Utilize “Catch-Up” Contributions:Individuals aged 50 and older can contribute an additional $1,500 to their Roth IRA in 2024. This “catch-up” contribution allows older individuals to make up for lost time and accelerate their retirement savings.
Comparison of Roth IRA to Other Retirement Savings Options
Comparing the Roth IRA to other retirement savings options is crucial for self-employed individuals. Here’s a breakdown:
| Retirement Savings Option | Contribution Type | Tax Treatment | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roth IRA | After-tax | Tax-free withdrawals in retirement | – Tax-free withdrawals in retirement
|
– Contributions are made with after-tax dollars
|
| Traditional IRA | Pre-tax | Taxable withdrawals in retirement | – Tax-deductible contributions
|
– Taxable withdrawals in retirement
When dealing with government agencies, it’s essential to understand the W9 Form requirements for October 2024. This form is crucial for providing your taxpayer identification number and other relevant information.
|
| Solo 401(k) | Pre-tax or Roth | Taxable or tax-free withdrawals in retirement | – Higher contribution limits than Roth IRAs
|
– More complex than Roth IRAs
|
Strategies for Efficient Retirement Savings, Roth IRA contribution limit for self-employed individuals in 2024
Self-employed individuals can implement various strategies to streamline their retirement savings:
- Automate Contributions:Setting up automatic contributions to your Roth IRA ensures consistent savings and eliminates the need for manual transfers.
- Utilize Tax Deductions:Self-employed individuals can deduct a portion of their contributions to a Solo 401(k) as a business expense, reducing their taxable income.
- Consult with a Financial Advisor:A financial advisor can help you create a comprehensive retirement plan tailored to your individual circumstances and goals.
Resources and Information
This section provides links to relevant resources, including IRS publications and websites, that offer detailed information on Roth IRA contributions for self-employed individuals. It also includes a table summarizing key information about Roth IRA contributions for self-employed individuals in 2024 and a flowchart illustrating the steps for contributing to a Roth IRA as a self-employed individual.
IRS Publications and Websites
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the primary source of information on Roth IRA contributions for self-employed individuals. Here are some helpful resources:
- IRS Publication 590-A, Contributions to Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs): This publication provides detailed information on Roth IRA contributions, including eligibility requirements, contribution limits, and tax implications. You can access it online at the IRS website or download a PDF version.
- IRS Website: The IRS website offers a wealth of information on Roth IRAs, including FAQs, tax forms, and other helpful resources. You can search for specific information using s or browse through the various categories on the website.
Key Information about Roth IRA Contributions for Self-Employed Individuals in 2024
The following table summarizes key information about Roth IRA contributions for self-employed individuals in 2024:
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Contribution Limit | $7,500 (for individuals under age 50) |
| Contribution Limit (Age 50 and Over) | $8,000 |
| Deductibility | Not deductible |
| Tax Implications | Distributions in retirement are tax-free |
Steps for Contributing to a Roth IRA as a Self-Employed Individual
The following flowchart illustrates the steps for contributing to a Roth IRA as a self-employed individual:
[Flowchart Illustration]
Conclusion
Contributing to a Roth IRA as a self-employed individual can be a powerful tool for building a secure financial future. By understanding the contribution limits, eligibility criteria, and tax implications, you can make informed decisions about your retirement savings. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to maximize your contributions, this guide provides the information you need to navigate the world of Roth IRA contributions for self-employed individuals.
Helpful Answers
What is the difference between a Roth IRA and a Traditional IRA for self-employed individuals?
The main difference lies in the tax treatment. Contributions to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax dollars, while contributions to a Traditional IRA are made with pre-tax dollars. Roth IRA withdrawals in retirement are tax-free, while Traditional IRA withdrawals are taxed.
How does the self-employed contribution limit work?
The contribution limit for self-employed individuals is calculated as a percentage of your adjusted net self-employment income. This means that your contribution limit may vary each year based on your income.
Are there any income limitations for contributing to a Roth IRA?
Yes, there are income limitations for contributing to a Roth IRA. If your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) exceeds a certain threshold, you may be phased out of contributing to a Roth IRA or your contribution may be limited.
What are some strategies for maximizing Roth IRA contributions?
Strategies include contributing early and often, taking advantage of catch-up contributions if you’re over 50, and carefully considering your income level to maximize your contribution potential.